|
|
|
Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system destroys its own healthy tissues. When this occurs, white blood cells cannot distinguish between pathogens and normal cells.
Adults are resistant to the bacterium that causes Botulism. These bacteria thrive in honey – therefore, honey should never be given to infants since their immune systems are not yet resistant.
Coca-Cola originally used coca leaves and caffeine from the African kola nut. It was advertised as a therapeutic agent and "pickerupper." Eventually, its formulation was changed, and the coca leaves were removed because of the effects of regulation on cocaine-related products.
Nitroglycerin is used to alleviate various heart-related conditions, and it is also the chief component of dynamite (but mixed in a solid clay base to stabilize it).
Critical care patients are twice as likely to receive the wrong medication. Of these errors, 20% are life-threatening, and 42% require additional life-sustaining treatments.
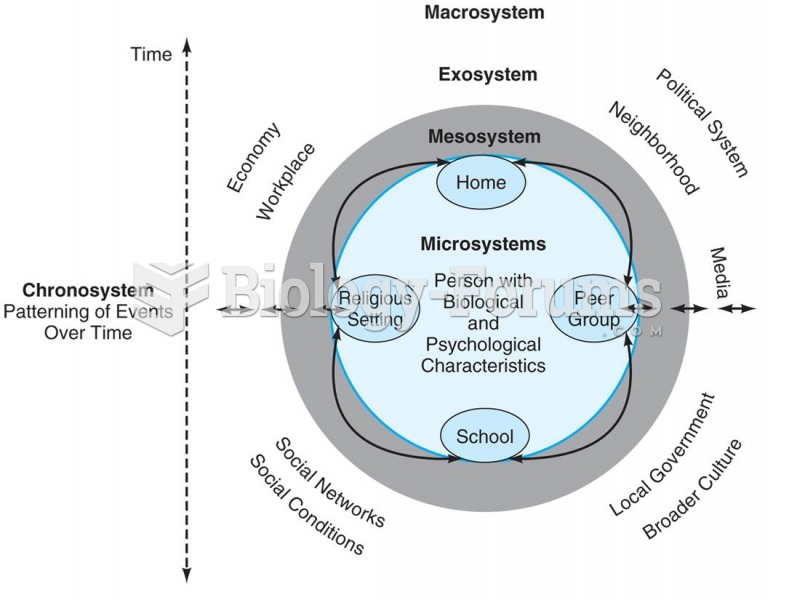 Bronfenbrenner’s model of the ecological-systems approach to studying development. He suggested that
Bronfenbrenner’s model of the ecological-systems approach to studying development. He suggested that
 Robert K. Merton (1910–2003), who spent most of his academic career at Columbia University, was a ...
Robert K. Merton (1910–2003), who spent most of his academic career at Columbia University, was a ...