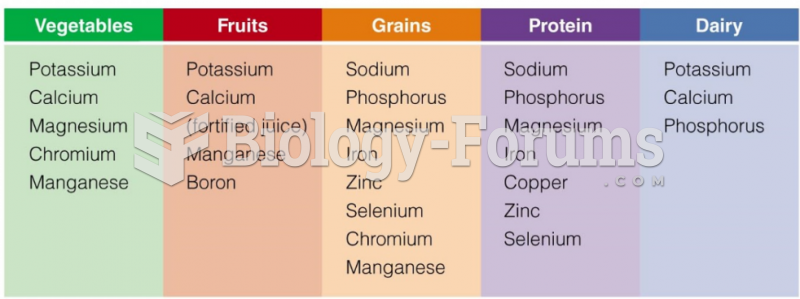
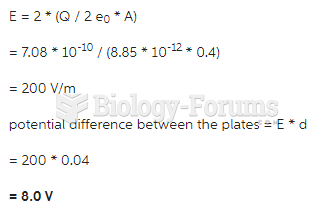
|
|
|
Aspirin is the most widely used drug in the world. It has even been recognized as such by the Guinness Book of World Records.
Drugs are in development that may cure asthma and hay fever once and for all. They target leukotrienes, which are known to cause tightening of the air passages in the lungs and increase mucus productions in nasal passages.
Amphetamine poisoning can cause intravascular coagulation, circulatory collapse, rhabdomyolysis, ischemic colitis, acute psychosis, hyperthermia, respiratory distress syndrome, and pericarditis.
Though “Krazy Glue” or “Super Glue” has the ability to seal small wounds, it is not recommended for this purpose since it contains many substances that should not enter the body through the skin, and may be harmful.
Acetaminophen (Tylenol) in overdose can seriously damage the liver. It should never be taken by people who use alcohol heavily; it can result in severe liver damage and even a condition requiring a liver transplant.
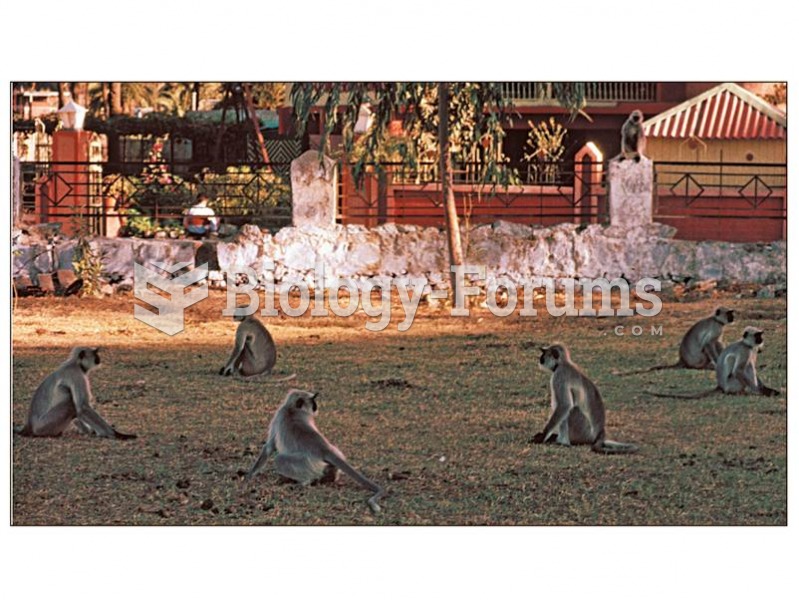 In one-male group species, extra males typically reside in all-male “bachelor” groups. These are Han
In one-male group species, extra males typically reside in all-male “bachelor” groups. These are Han
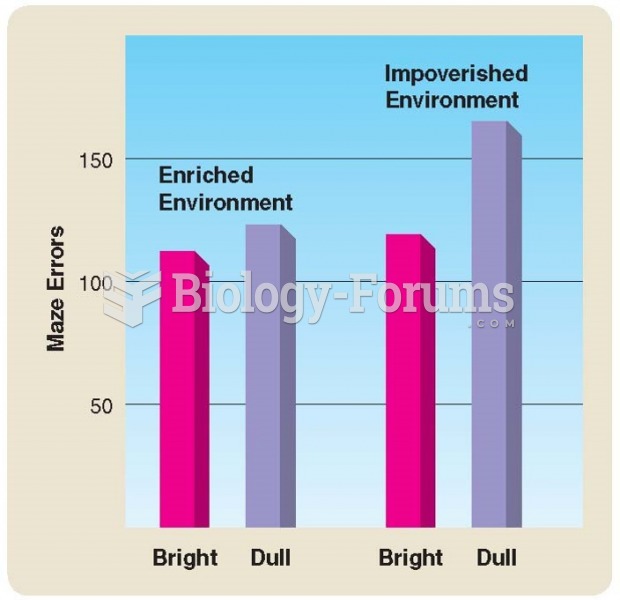 Maze-dull rats did not make significantly more errors than maze-bright rats when both groups were ...
Maze-dull rats did not make significantly more errors than maze-bright rats when both groups were ...