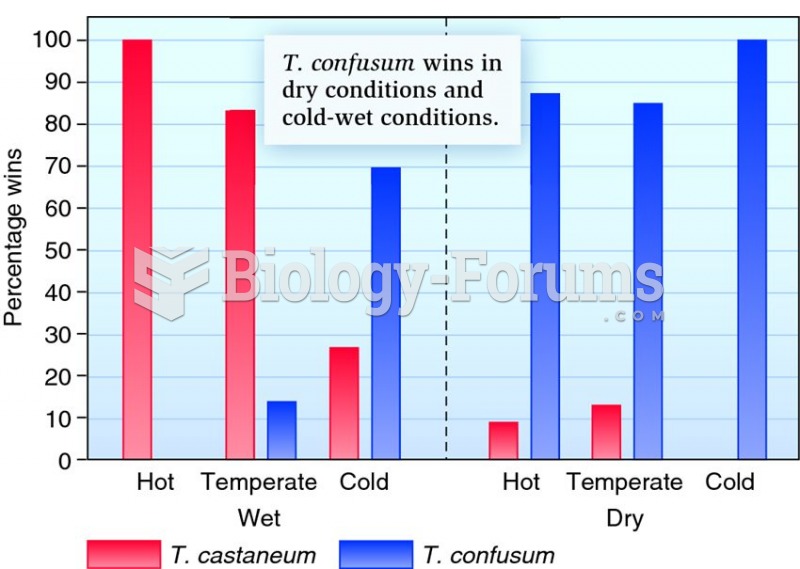
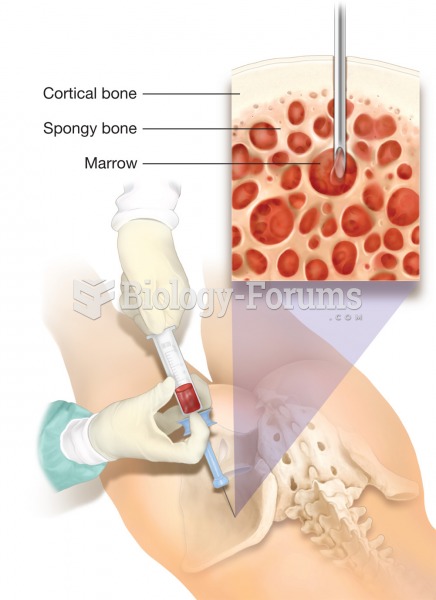
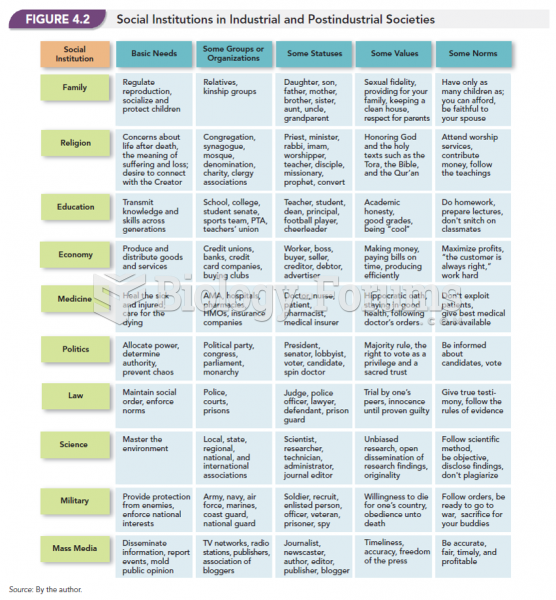
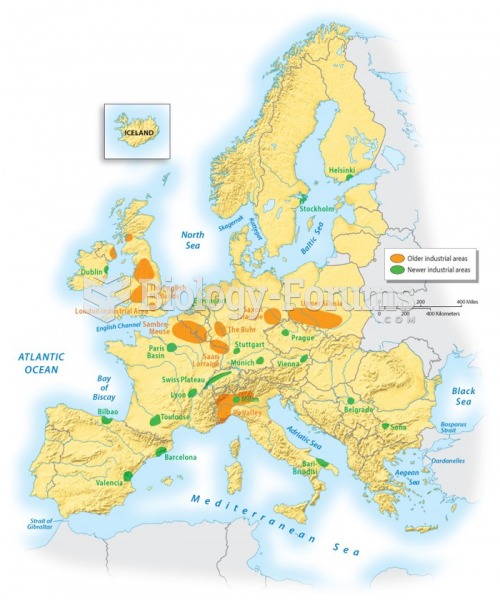
Answer to Question 1
In the old days, when China still had a planned economy, Beijing was able to exert leverage over local governments by threatening to deny them important economic benefits, but as the planned economy was phased out during the 1980s and the 1990s, Beijing found itself in a situation where it had to take local government considerations increasingly into account in order to expect its policies to be implemented locally. But local governments do not simply manipulate orders from on high; more recently, local governments have become increasingly aggressive in influencing the policy process. In Beijing, there are an evergrowing number of local government liaison offices in which representatives of local governments can monitor and influence the decision making that occurs in the capital. Moreover, local governments (and their constituents) from the interior are becoming increasingly vocal, particularly those that largely missed out on the economic boom of the 1990s.
Despite the common perception that the media is tightly controlled in China, China's citizens often have access to a great deal of information, although official censorship continues to limit certain type of information from getting through. Although it is important to avoid overstating the growing parameters of acceptable discourse in China, newspapers, magazines, and television broadcasts have provided a platform for journalists to pursue stories that match their own increasingly progressive interests and agendas. Moreover, during the reform era, media outlets have been increasingly responsible for their own bottom lines and can no longer depend on state budgetary allocations to cover their operating costs. As a result, they must rely on advertisers and, thus, they now carry stories that people are interested in consuming. Very often, this means an increasing focus on controversial subjects, including government injustice, civil protest, and the like.
Industrial and professional groups that seek to influence policy are also often consulted by the government during the law and policymaking process. These include multiple industry groups in sectors as diverse as steel, consumer electronics, and computer software. Many business associations that lobby the Chinese government can point to some modest successes in influencing policy, or, at the very least, are now able to sit in on the policymaking process.
Though China is a oneparty authoritarian state, nongovernmental organizations (NGOs) have also proliferated in China. These associations run the gamut from foreign and domestic business groups in Beijing and Shanghai that seek better intellectual property protection, to ruralbased environmental NGOs in the backwoods. One particularly important node of the media's power is the close relationship it shares with many Chinese nongovernmental organizations, and one thing that accounts for the successes of NGOs in Chinese politics is that a large percentage of their officers and staff members were trained as journalists or editors, giving them especially close access to the media. Legal institutions also have abounded with lawyers and other legal specialists working together with the Chinese government (and particularly the National People's Congress, China's legislative body) to establish laws and regulations as well as to educate Chinese officials.
Answer to Question 2
False