|
|
|
Aspirin may benefit 11 different cancers, including those of the colon, pancreas, lungs, prostate, breasts, and leukemia.
Serum cholesterol testing in adults is recommended every 1 to 5 years. People with diabetes and a family history of high cholesterol should be tested even more frequently.
Though methadone is often used to treat dependency on other opioids, the drug itself can be abused. Crushing or snorting methadone can achieve the opiate "rush" desired by addicts. Improper use such as these can lead to a dangerous dependency on methadone. This drug now accounts for nearly one-third of opioid-related deaths.
Fatal fungal infections may be able to resist newer antifungal drugs. Globally, fungal infections are often fatal due to the lack of access to multiple antifungals, which may be required to be utilized in combination. Single antifungals may not be enough to stop a fungal infection from causing the death of a patient.
The term bacteria was devised in the 19th century by German biologist Ferdinand Cohn. He based it on the Greek word "bakterion" meaning a small rod or staff. Cohn is considered to be the father of modern bacteriology.
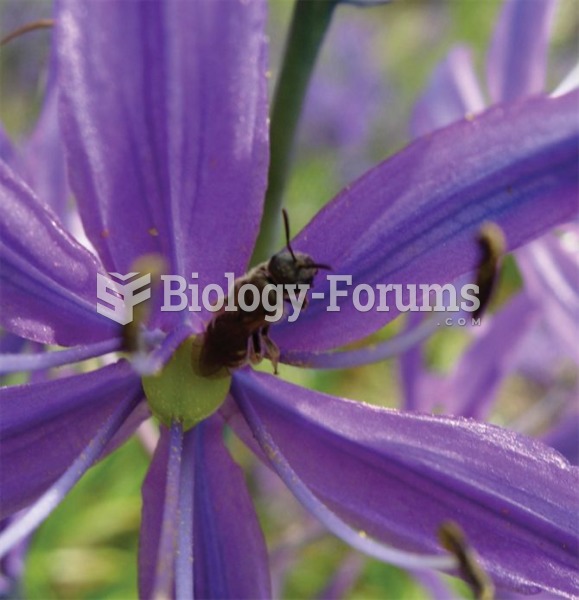 Mutualisms, such as those that occur among plants and pollinators, generally involve large numbers o
Mutualisms, such as those that occur among plants and pollinators, generally involve large numbers o
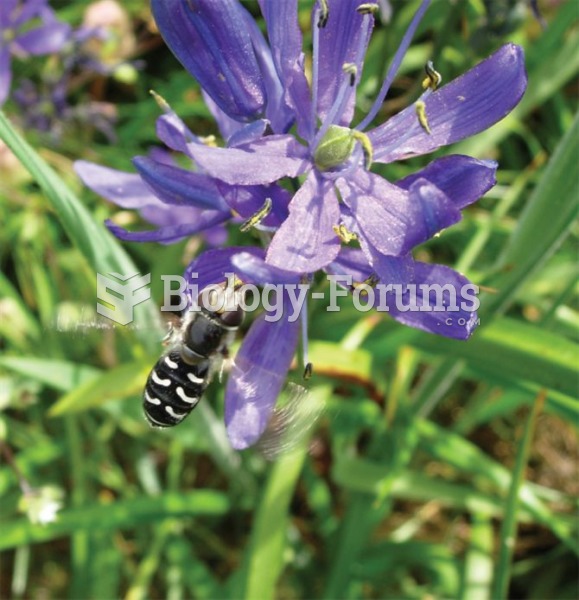 Mutualisms, such as those that occur among plants and pollinators, generally involve large numbers o
Mutualisms, such as those that occur among plants and pollinators, generally involve large numbers o
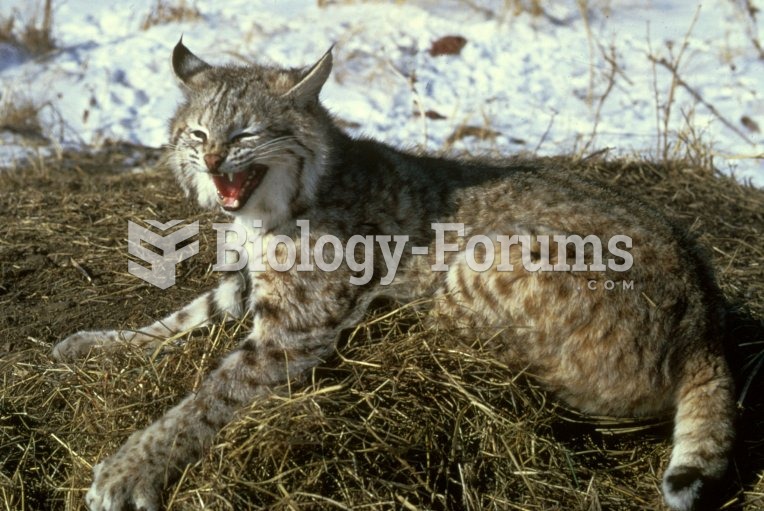 The bobcat population has seen declines in the American Midwest, but is generally stable and healthy
The bobcat population has seen declines in the American Midwest, but is generally stable and healthy
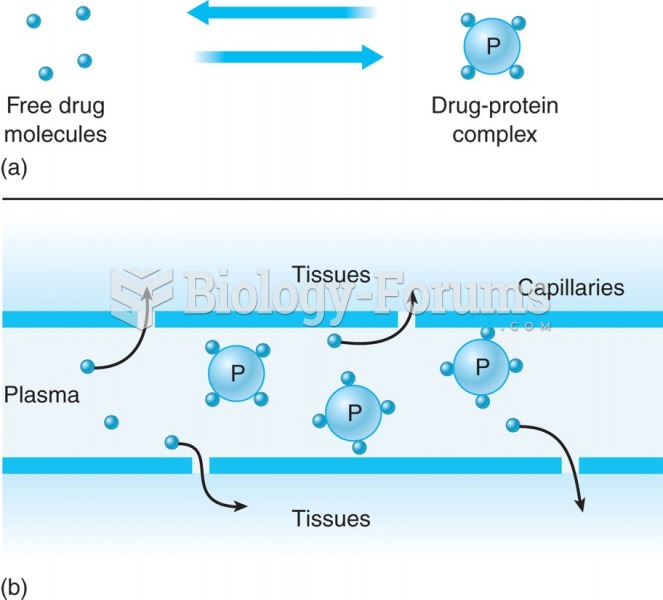
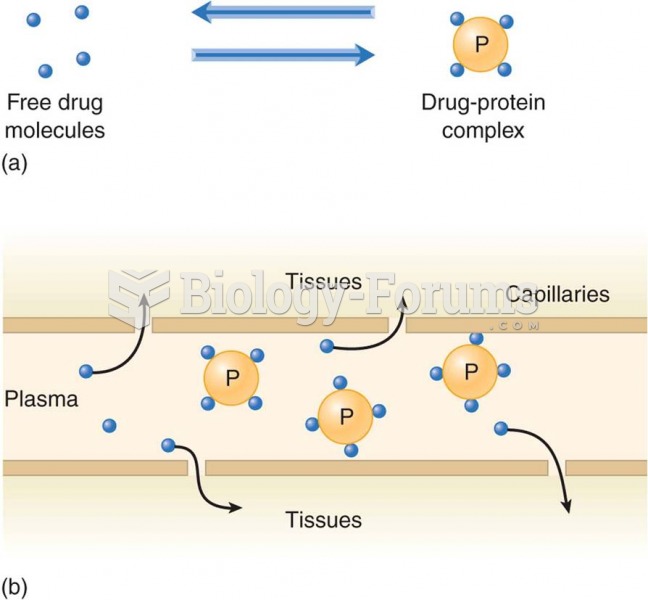 Plasma protein binding and drug availability: (a) drug exists in a free state or bound to plasma pro
Plasma protein binding and drug availability: (a) drug exists in a free state or bound to plasma pro