|
|
|
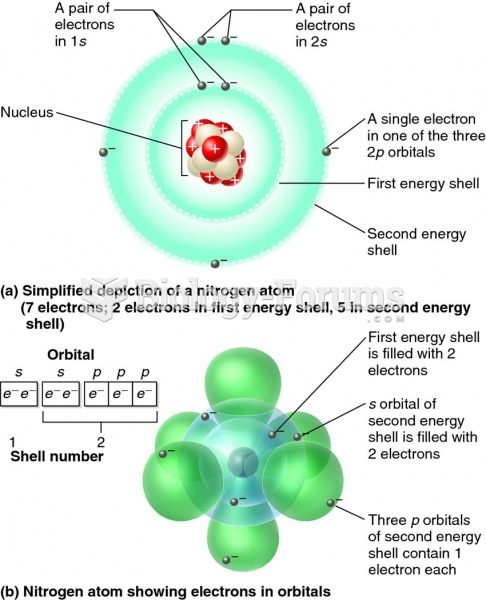
The term bacteria was devised in the 19th century by German biologist Ferdinand Cohn. He based it on the Greek word "bakterion" meaning a small rod or staff. Cohn is considered to be the father of modern bacteriology.
More than 4.4billion prescriptions were dispensed within the United States in 2016.
Though newer “smart” infusion pumps are increasingly becoming more sophisticated, they cannot prevent all programming and administration errors. Health care professionals that use smart infusion pumps must still practice the rights of medication administration and have other professionals double-check all high-risk infusions.
The toxic levels for lithium carbonate are close to the therapeutic levels. Signs of toxicity include fine hand tremor, polyuria, mild thirst, nausea, general discomfort, diarrhea, vomiting, drowsiness, muscular weakness, lack of coordination, ataxia, giddiness, tinnitus, and blurred vision.
Ether was used widely for surgeries but became less popular because of its flammability and its tendency to cause vomiting. In England, it was quickly replaced by chloroform, but this agent caused many deaths and lost popularity.