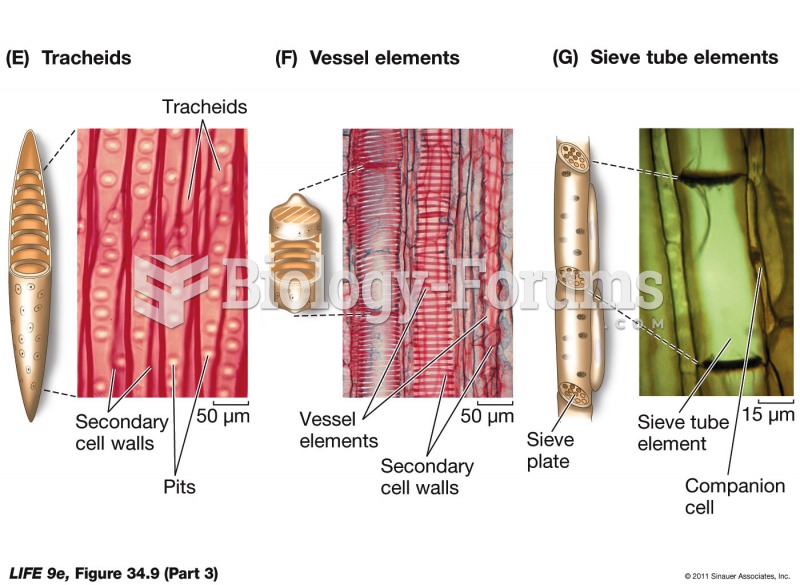
Answer to Question 1
An ideal response will:
1, Define an interest group as a group or organization that advocates and lobbies for policies that will meet its particular interests and needs.
2, Describe ethnic lobbies as interest groups that advocate for policies focusing on specific foreign states, such as foreign aid to a country or pressure against a foreign state's governing regime.
3, Discuss business groups as interest groups that lobby for policies favorable to their business interests, such as an increase in defense spending that would benefit companies producing or selling military goods or free trade discussions with a country in which a multinational corporation is interested in doing business.
4, Identify think tanks as groups that support and publicize the work of scholars, many of whom have foreign policy expertise, and that may seek to alter public opinion and put pressure on the government by offering foreign policy insights and opinions.
5, Outline an example of an ethnic lobby's interest in Iran, for example, a group with ties to Israel might lobby for the United States to send weapons to Israel so that the country can protect itself from Iran.
6, Provide an example of a business group's interest in Iran, for example, a multinational oil company might lobby for diplomatic measures rather than economic sanctions or military intervention to prevent having the company's oil supply disrupted.
7, Note an example of how a think tank might become involved in the Iran issue, for example, by publishing articles about the pressing need to stop nuclear proliferation and encouraging the public to pressure the government for stronger interventions, whether through economic sanctions or even military action if needed.
Answer to Question 2
An ideal response will:
1, Describe the policy reforms initiated following 9/11, including the reorganization of the federal bureaucracy so that various intelligence and law enforcement agencies would be better coordinated and engage in greater intelligence information sharing.
2, Note that since 9/11, the U.S. government has successfully thwarted several high-profile terrorist plots.
3, Explain at least two challenges in determining whether the federal bureaucracy deserves credit for preventing subsequent terrorist attacks, including the difficulty of separating the policies created by Congress and the president from their implementation by the bureaucracy and the difficulty of determining the size of the terrorist threat.