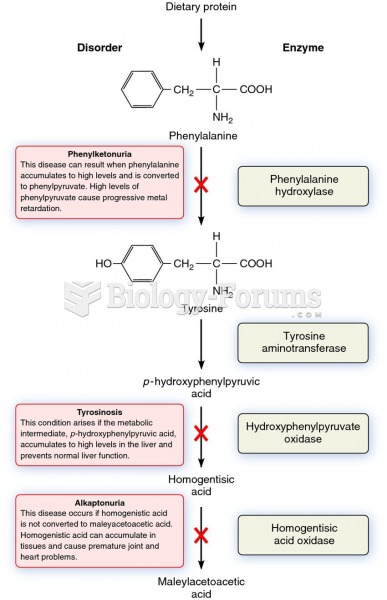
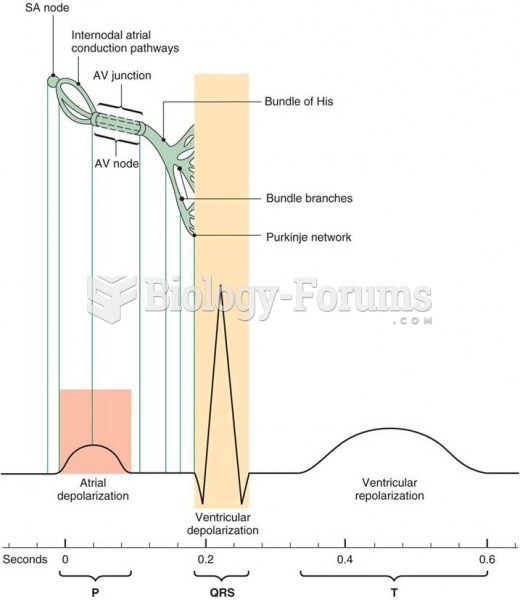
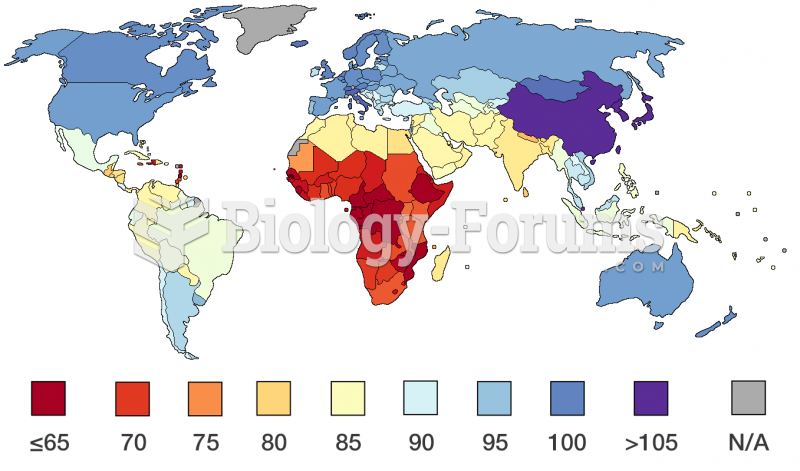
Answer to Question 1
Answer:
An ideal response will:
1. Define de facto segregation as racial imbalances not directly caused by official actions but rather by residential patterns.
2. Explain how in Plessy v. Ferguson, the Supreme Court upheld state laws requiring segregation in effect giving constitutional approval to segregation.
3. Explain how the decision in Brown v. Board of Education overturned the separate-but-equal doctrine, rejecting segregation sanctioned by law in the field of public education.
4. Evaluate whether citizens' private decisions to segregate lead to inequality. Those who believe that it does may point to the same logic used by the Supreme Court in Brown v. Board of Education. Those who believe that it does not may point to the fact that the two concepts are completely distinct: Individuals can be both segregated and equal or both integrated and unequal.
5. Illustrate the relationship between de facto segregation and inequality with two examples. For example, describe whether residential neighborhoods and churches (two entities with de facto segregation) promote inequality.
Answer to Question 2
Answer:
An ideal response will:
1. Detail the accommodation to segregation response of Washington who was the foremost African American advocate of accommodation to segregation. His hopes for black America lay in a program of self-help through education. Washington urged his students to stay in the South, acquire land, and build homes, thereby helping eliminate ignorance and poverty and in effect, making the best of segregation. Combined with the approach of W.E.B. Du Bois, of black resistance, protest, and the political mobilization of blacks in the North, the civil rights movement moved forward.
2. Describe how the movement for gay rights similarly involved a quiet, conformist approach advanced by groups such as Mattachine. The conservative, nearly philosophical approach to protest and recognition was overwhelmed by openly gay, openly identified groups that refused to minimize sexuality in their organizations or their movement. The riots at Stonewall was a rebellion reflecting that the movement for gay rights was not governed by quiet, assimilative strategies but by demands for open recognition in society and under the law.
3. Make connections between the assimilation and protest approaches present in each movement for civil rights.