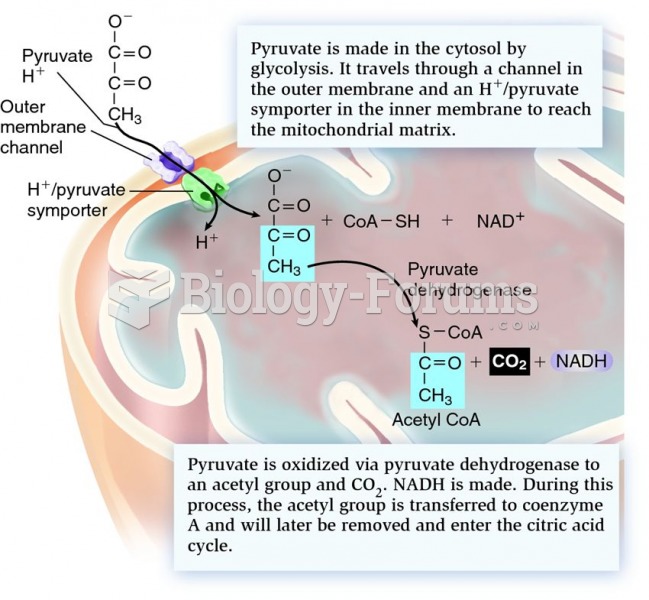
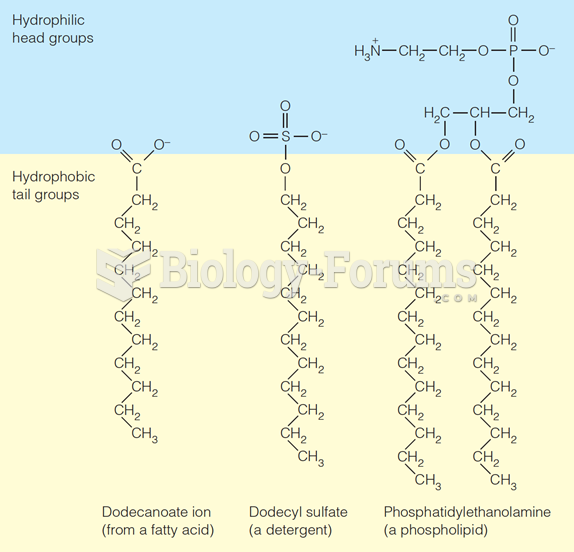
|
|
|
Cocaine was isolated in 1860 and first used as a local anesthetic in 1884. Its first clinical use was by Sigmund Freud to wean a patient from morphine addiction. The fictional character Sherlock Holmes was supposed to be addicted to cocaine by injection.
Chronic necrotizing aspergillosis has a slowly progressive process that, unlike invasive aspergillosis, does not spread to other organ systems or the blood vessels. It most often affects middle-aged and elderly individuals, spreading to surrounding tissue in the lungs. The disease often does not respond to conventionally successful treatments, and requires individualized therapies in order to keep it from becoming life-threatening.
Stevens-Johnson syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis syndrome are life-threatening reactions that can result in death. Complications include permanent blindness, dry-eye syndrome, lung damage, photophobia, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, permanent loss of nail beds, scarring of mucous membranes, arthritis, and chronic fatigue syndrome. Many patients' pores scar shut, causing them to retain heat.
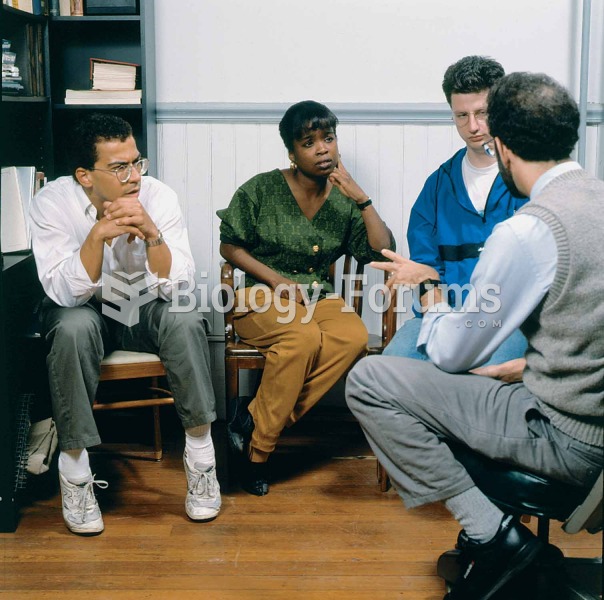
Medication errors are three times higher among children and infants than with adults.
Blood is approximately twice as thick as water because of the cells and other components found in it.