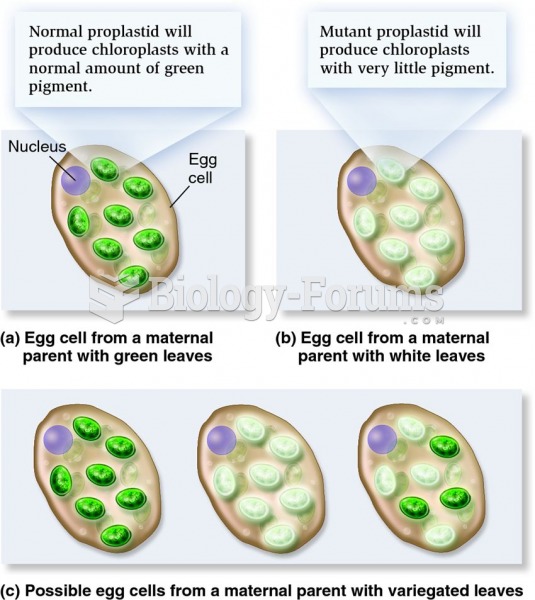
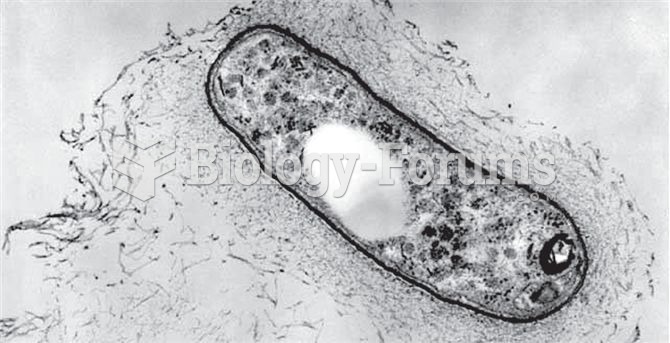
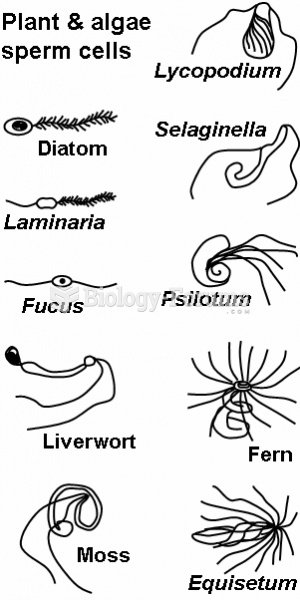
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
The average office desk has 400 times more bacteria on it than a toilet.
Did you know?
The first documented use of surgical anesthesia in the United States was in Connecticut in 1844.
Did you know?
The modern decimal position system was the invention of the Hindus (around 800 AD), involving the placing of numerals to indicate their value (units, tens, hundreds, and so on).
Did you know?
Between 1999 and 2012, American adults with high total cholesterol decreased from 18.3% to 12.9%
Did you know?
Individuals are never “cured” of addictions. Instead, they learn how to manage their disease to lead healthy, balanced lives.