This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
It is important to read food labels and choose foods with low cholesterol and saturated trans fat. You should limit saturated fat to no higher than 6% of daily calories.
Did you know?
Thyroid conditions cause a higher risk of fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue syndrome.
Did you know?
Earwax has antimicrobial properties that reduce the viability of bacteria and fungus in the human ear.
Did you know?
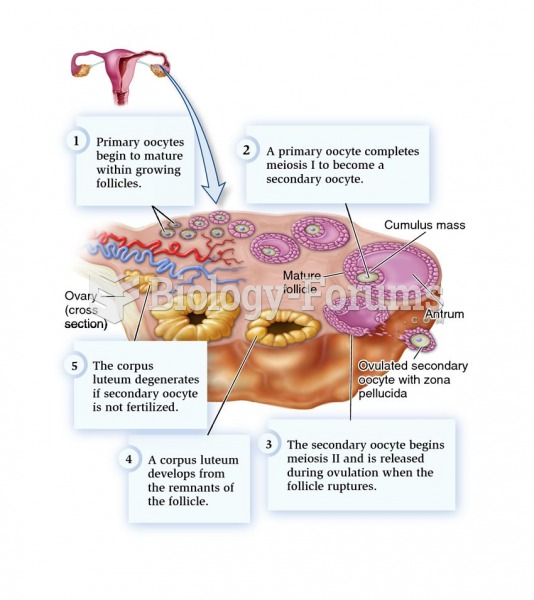
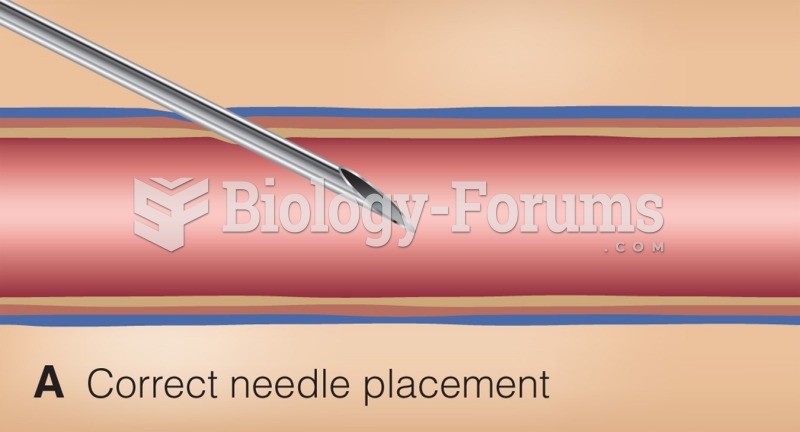
Many medications that are used to treat infertility are injected subcutaneously. This is easy to do using the anterior abdomen as the site of injection but avoiding the area directly around the belly button.
Did you know?
Cancer has been around as long as humankind, but only in the second half of the twentieth century did the number of cancer cases explode.