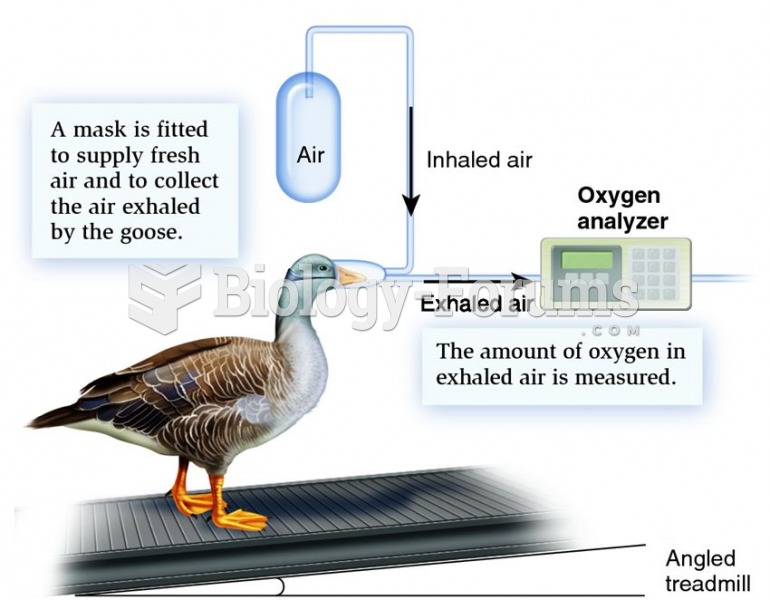
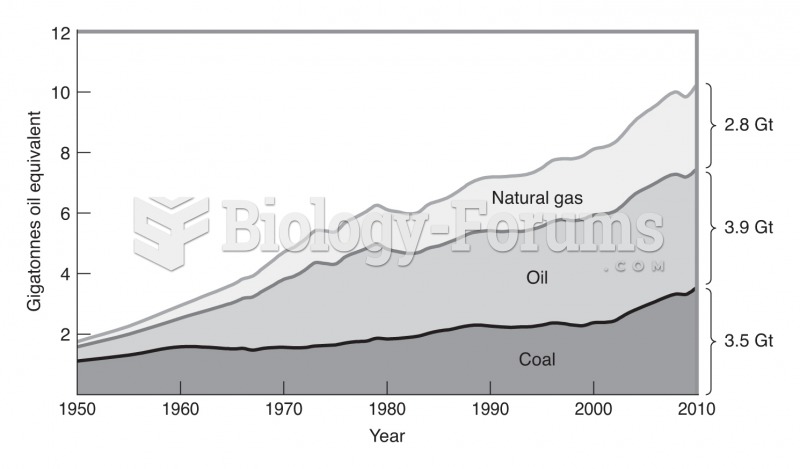
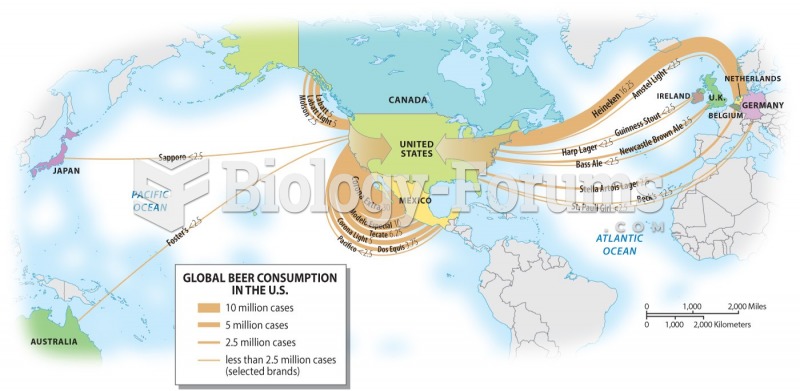
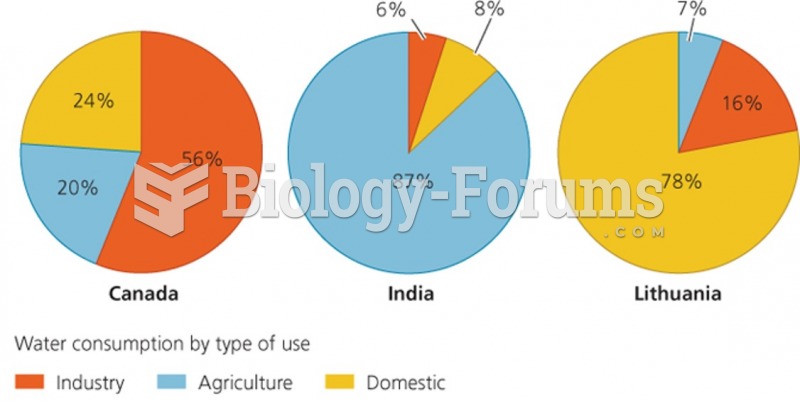
|
|
|
In 1835 it was discovered that a disease of silkworms known as muscardine could be transferred from one silkworm to another, and was caused by a fungus.
Aspirin is the most widely used drug in the world. It has even been recognized as such by the Guinness Book of World Records.
Drugs are in development that may cure asthma and hay fever once and for all. They target leukotrienes, which are known to cause tightening of the air passages in the lungs and increase mucus productions in nasal passages.
Astigmatism is the most common vision problem. It may accompany nearsightedness or farsightedness. It is usually caused by an irregularly shaped cornea, but sometimes it is the result of an irregularly shaped lens. Either type can be corrected by eyeglasses, contact lenses, or refractive surgery.
As many as 28% of hospitalized patients requiring mechanical ventilators to help them breathe (for more than 48 hours) will develop ventilator-associated pneumonia. Current therapy involves intravenous antibiotics, but new antibiotics that can be inhaled (and more directly treat the infection) are being developed.