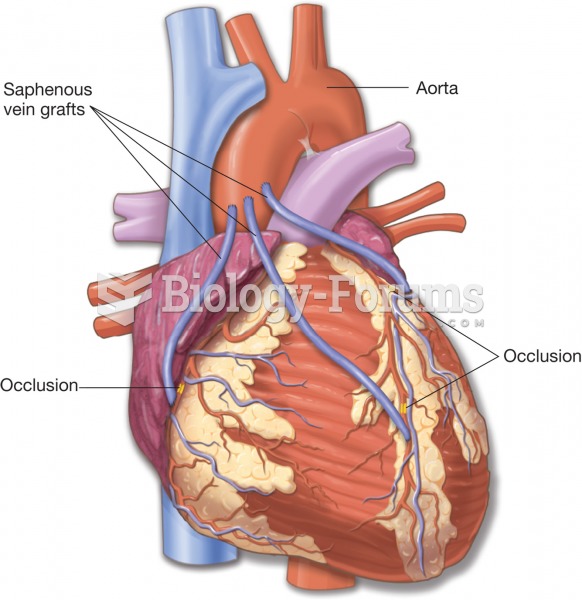
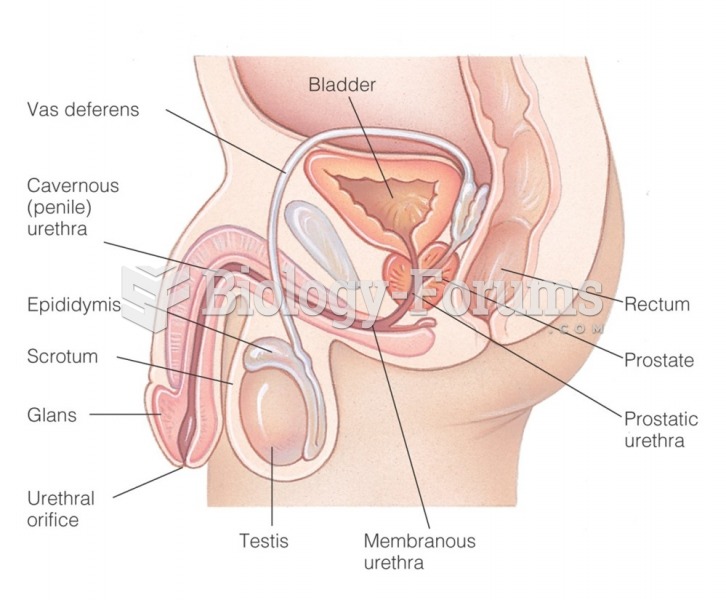
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Calcitonin is a naturally occurring hormone. In women who are at least 5 years beyond menopause, it slows bone loss and increases spinal bone density.
Did you know?
It is difficult to obtain enough calcium without consuming milk or other dairy foods.
Did you know?
The newest statin drug, rosuvastatin, has been called a superstatin because it appears to reduce LDL cholesterol to a greater degree than the other approved statin drugs.
Did you know?
The ratio of hydrogen atoms to oxygen in water (H2O) is 2:1.
Did you know?
Critical care patients are twice as likely to receive the wrong medication. Of these errors, 20% are life-threatening, and 42% require additional life-sustaining treatments.