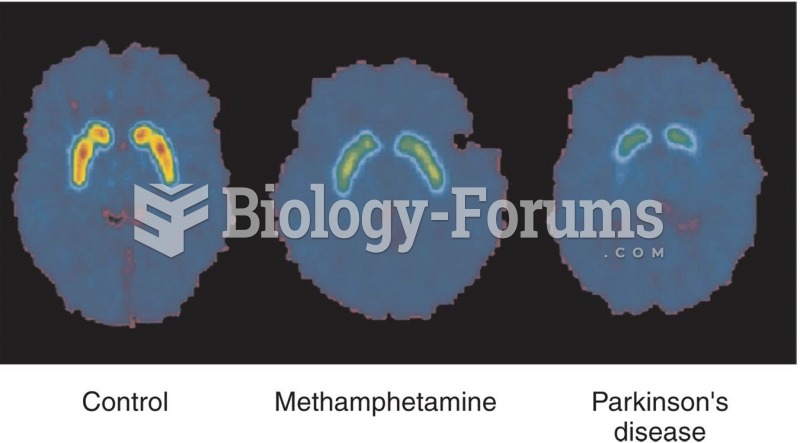
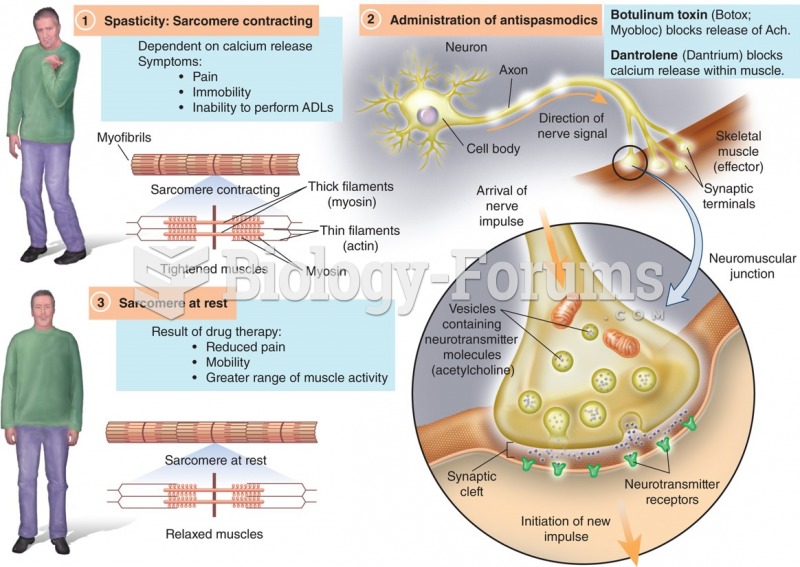
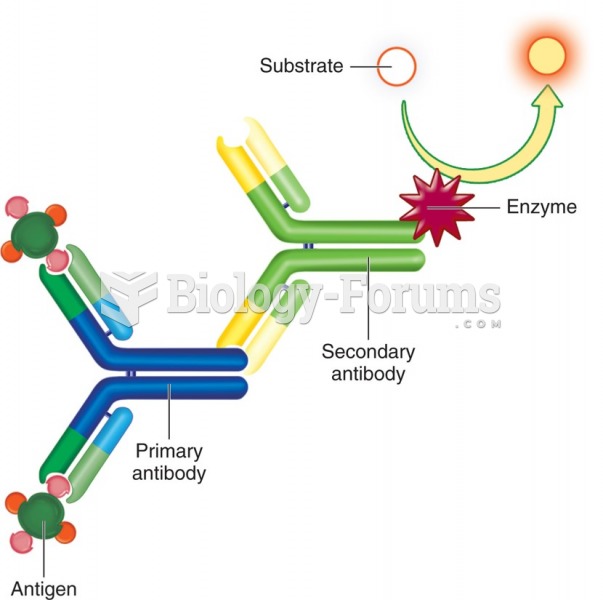
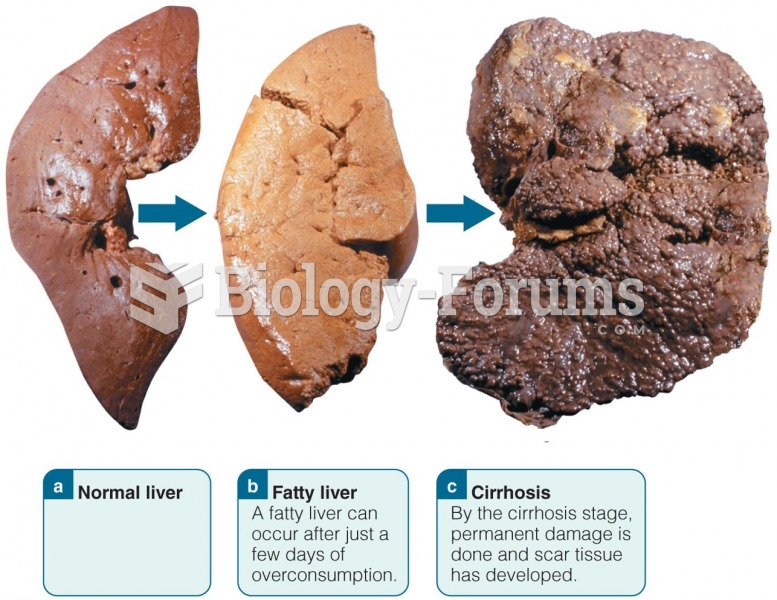
|
|
|
Did you know?
In most climates, 8 to 10 glasses of water per day is recommended for adults. The best indicator for adequate fluid intake is frequent, clear urination.
Did you know?
Normal urine is sterile. It contains fluids, salts, and waste products. It is free of bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
Did you know?
The first successful kidney transplant was performed in 1954 and occurred in Boston. A kidney from an identical twin was transplanted into his dying brother's body and was not rejected because it did not appear foreign to his body.
Did you know?
Bacteria have been found alive in a lake buried one half mile under ice in Antarctica.
Did you know?
There are 60,000 miles of blood vessels in every adult human.