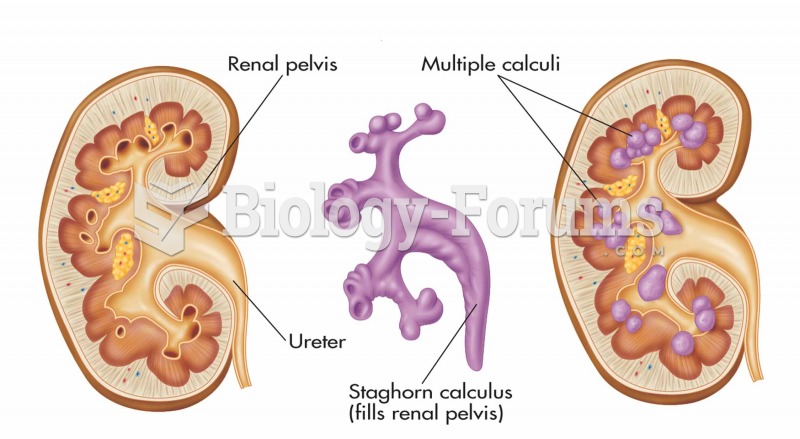
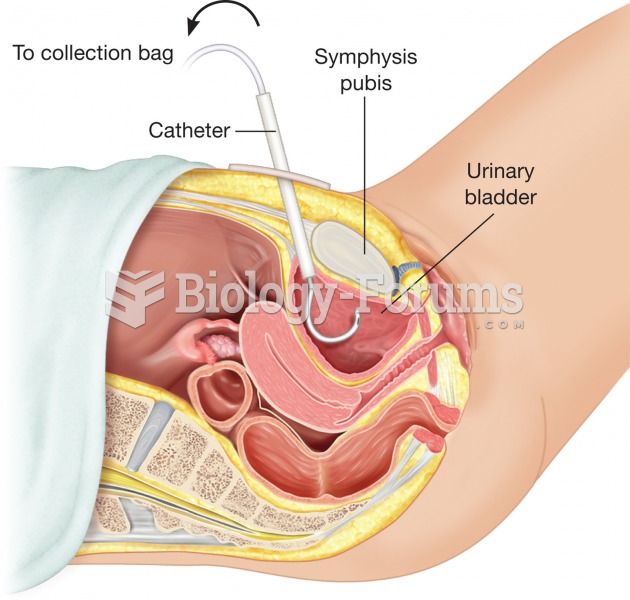
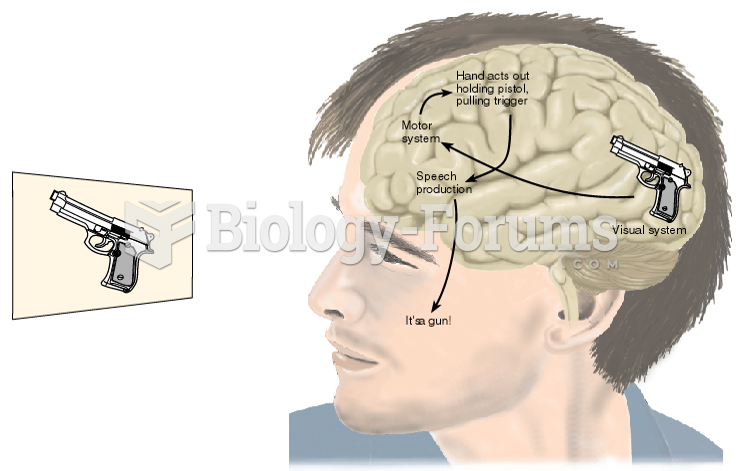
|
|
|
The shortest mature adult human of whom there is independent evidence was Gul Mohammed in India. In 1990, he was measured in New Delhi and stood 22.5 inches tall.
To prove that stomach ulcers were caused by bacteria and not by stress, a researcher consumed an entire laboratory beaker full of bacterial culture. After this, he did indeed develop stomach ulcers, and won the Nobel Prize for his discovery.
It is important to read food labels and choose foods with low cholesterol and saturated trans fat. You should limit saturated fat to no higher than 6% of daily calories.
Russia has the highest death rate from cardiovascular disease followed by the Ukraine, Romania, Hungary, and Poland.
The senior population grows every year. Seniors older than 65 years of age now comprise more than 13% of the total population. However, women outlive men. In the 85-and-over age group, there are only 45 men to every 100 women.