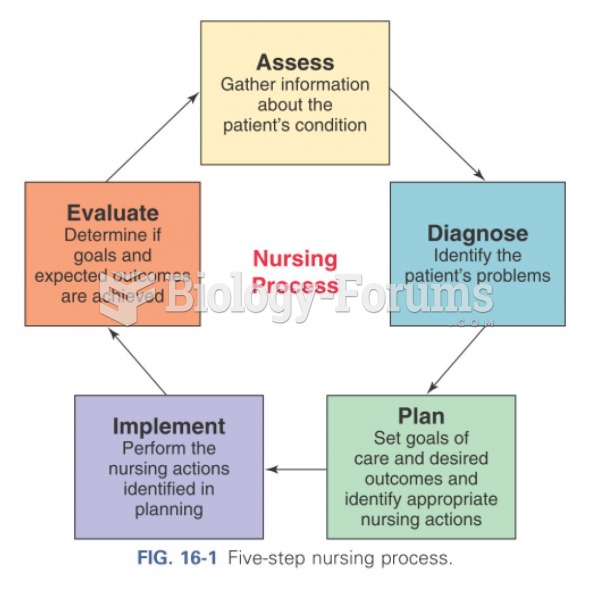
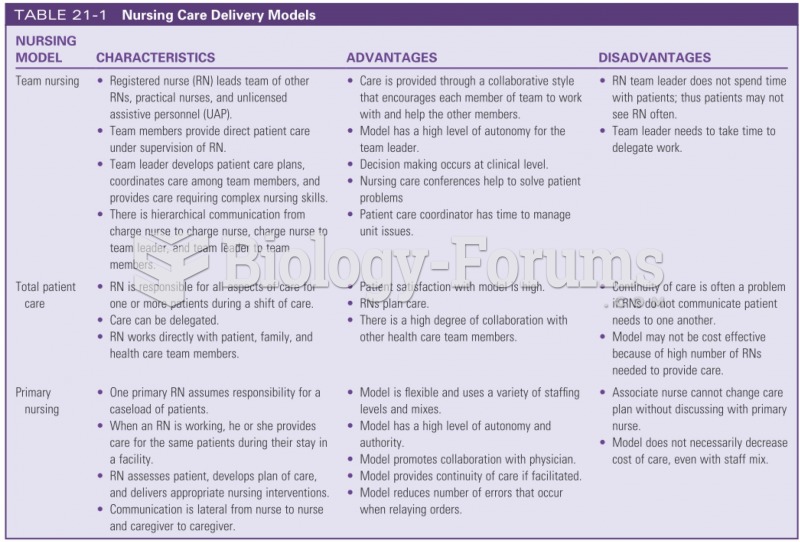
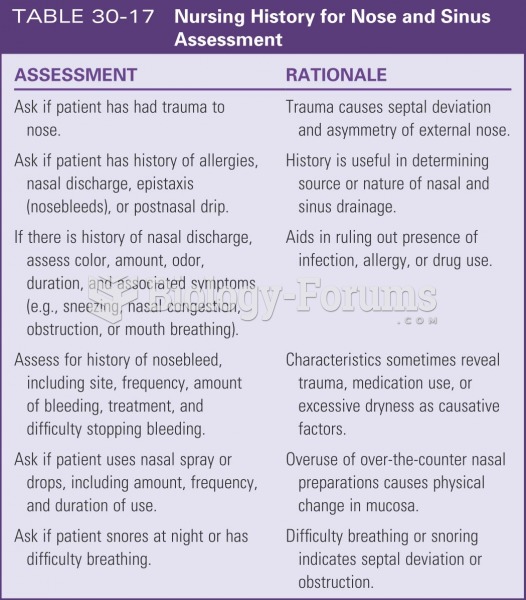
Answer to Question 1
B
Feedback
A Incorrect. The nurse avoids assigning more than three residents to the assistants for feeding; four residents are too many to assist safely.
B Correct. With adequate training and cooperation, the nurse allows family mem-bers to feed residents who need assistance with feeding. While the family is as-sisting with feeding, the nurse supervises the feeding, offers feedback to family members if necessary, and evaluates the outcome.
C Incorrect. If a resident needs assistance with feeding, it can be dangerous, humi-liating, and frustrating for a resident to attempt self-feeding.
D Incorrect. If a small group of assistants performs all of the feeding, then the res-idents will potentially have to wait for long periods before being fed. Since the time required to implement feeding assistance is 38 minutes, a lengthy delay can result in adverse effects or injury for the resident and increase the risk of errors for the assistants and lead to frustration with the residents.
Answer to Question 2
B
The Confusion Assessment Method is a tool for measuring delirium in patients who are intubated or nonverbal. Assessing the accessory (CN XI) and hypoglossal (CN XII) cranial nerves provides clues about the patient's ability to swallow. The nurse uses the Controlled Word Association Test to assess for a neurologic cause of an older adult's cognitive dysfunction. This tool is an index of frontal lobe functioning and provides an assessment of executive function, including the patient's frontal lobe functioning and his or her ability to refrain from distraction and perseveration. The MMSE-2 is a valid and reliable tool to assess cognitive function; however, it is unable to pinpoint discrete areas of neurologic dysfunction.