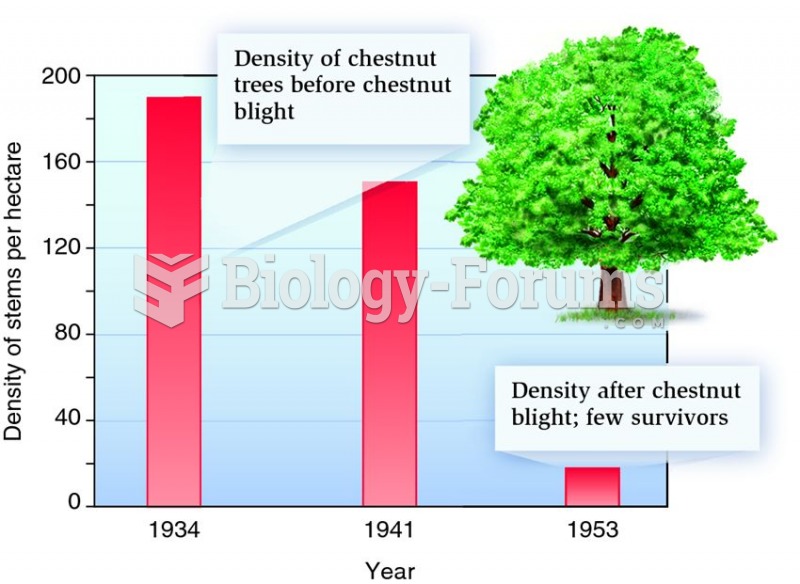
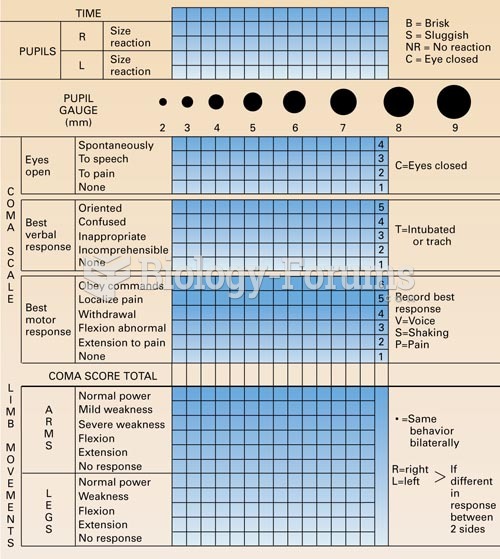
|
|
|
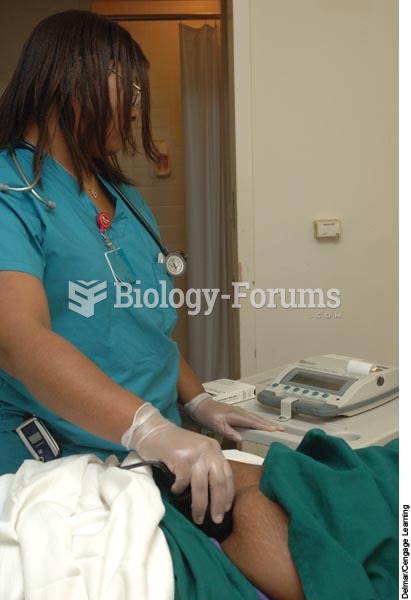
Automated pill dispensing systems have alarms to alert patients when the correct dosing time has arrived. Most systems work with many varieties of medications, so patients who are taking a variety of drugs can still be in control of their dose regimen.
Certain topical medications such as clotrimazole and betamethasone are not approved for use in children younger than 12 years of age. They must be used very cautiously, as directed by a doctor, to treat any child. Children have a much greater response to topical steroid medications.
The heart is located in the center of the chest, with part of it tipped slightly so that it taps against the left side of the chest.
Your skin wrinkles if you stay in the bathtub a long time because the outermost layer of skin (which consists of dead keratin) swells when it absorbs water. It is tightly attached to the skin below it, so it compensates for the increased area by wrinkling. This happens to the hands and feet because they have the thickest layer of dead keratin cells.
The senior population grows every year. Seniors older than 65 years of age now comprise more than 13% of the total population. However, women outlive men. In the 85-and-over age group, there are only 45 men to every 100 women.