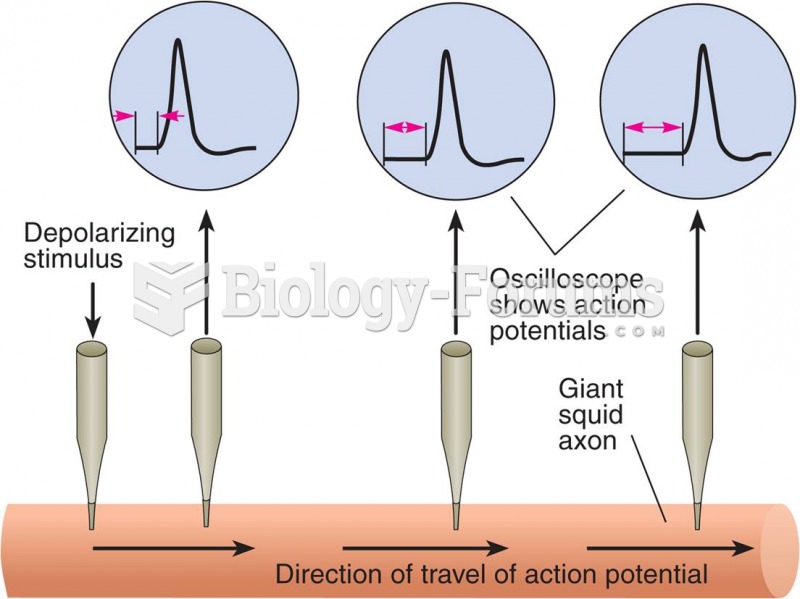
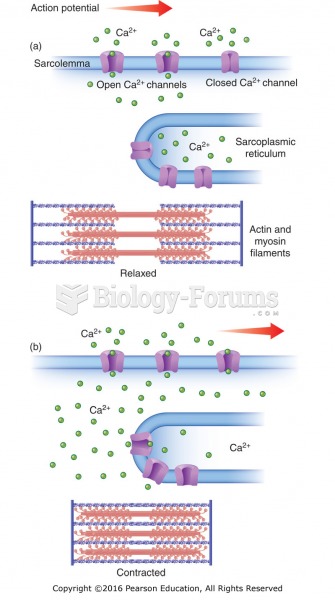
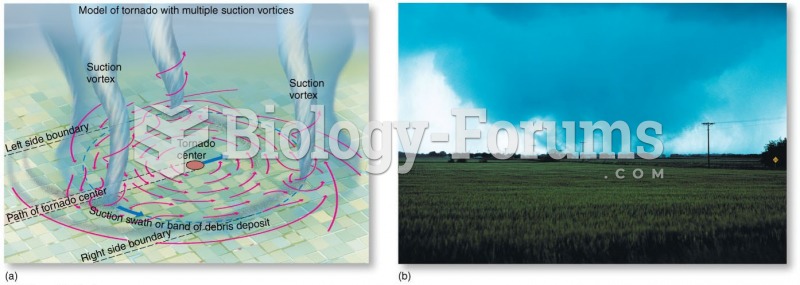
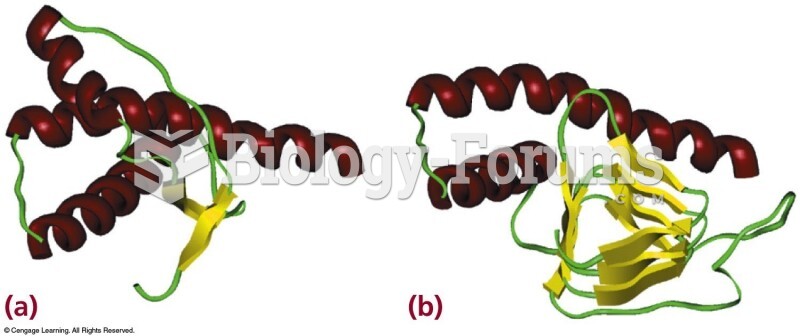
|
|
|
When intravenous medications are involved in adverse drug events, their harmful effects may occur more rapidly, and be more severe than errors with oral medications. This is due to the direct administration into the bloodstream.
A good example of polar molecules can be understood when trying to make a cake. If water and oil are required, they will not mix together. If you put them into a measuring cup, the oil will rise to the top while the water remains on the bottom.
There are immediate benefits of chiropractic adjustments that are visible via magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). It shows that spinal manipulation therapy is effective in decreasing pain and increasing the gaps between the vertebrae, reducing pressure that leads to pain.
Every 10 seconds, a person in the United States goes to the emergency room complaining of head pain. About 1.2 million visits are for acute migraine attacks.
To prove that stomach ulcers were caused by bacteria and not by stress, a researcher consumed an entire laboratory beaker full of bacterial culture. After this, he did indeed develop stomach ulcers, and won the Nobel Prize for his discovery.