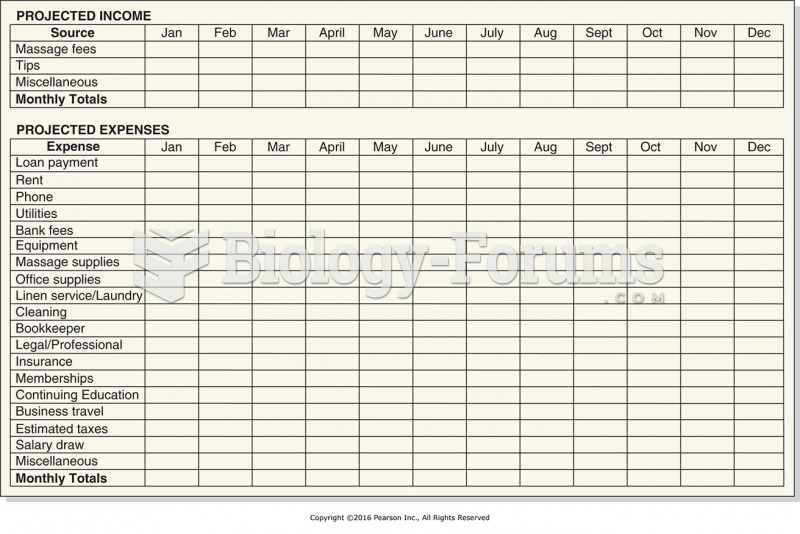
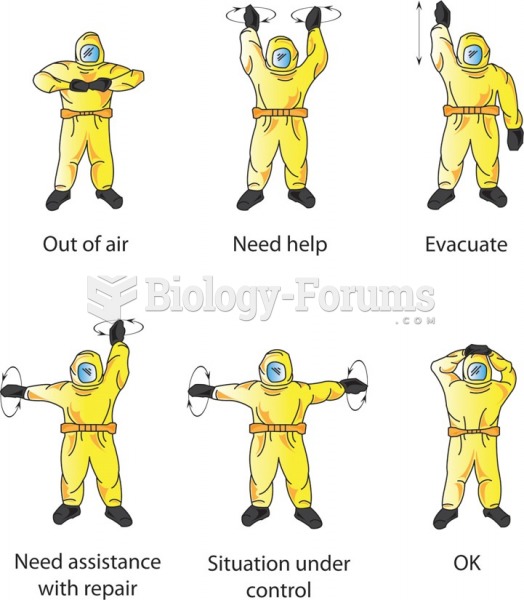
|
|
|
A seasonal flu vaccine is the best way to reduce the chances you will get seasonal influenza and spread it to others.
For about 100 years, scientists thought that peptic ulcers were caused by stress, spicy food, and alcohol. Later, researchers added stomach acid to the list of causes and began treating ulcers with antacids. Now it is known that peptic ulcers are predominantly caused by Helicobacter pylori, a spiral-shaped bacterium that normally exist in the stomach.
There are actually 60 minerals, 16 vitamins, 12 essential amino acids, and three essential fatty acids that your body needs every day.
HIV testing reach is still limited. An estimated 40% of people with HIV (more than 14 million) remain undiagnosed and do not know their infection status.
When taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors, people should avoid a variety of foods, which include alcoholic beverages, bean curd, broad (fava) bean pods, cheese, fish, ginseng, protein extracts, meat, sauerkraut, shrimp paste, soups, and yeast.
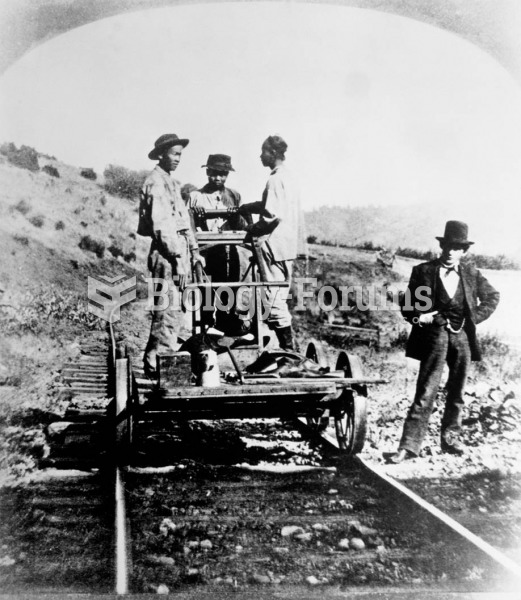 Chinese workers on a railway in the far West. “Without them,” Leland Stanford, president of the Cent
Chinese workers on a railway in the far West. “Without them,” Leland Stanford, president of the Cent
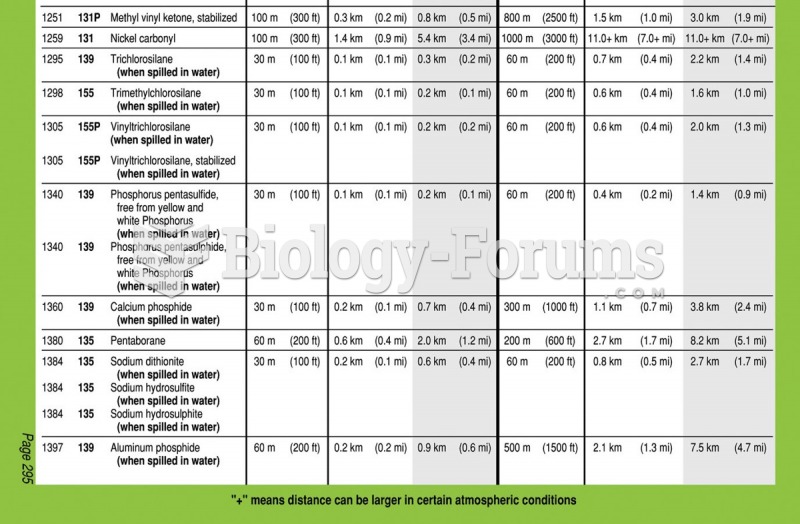 The yellow, blue, and green sections of the Emergency Response Guidebook (ERG). The yellow section ...
The yellow, blue, and green sections of the Emergency Response Guidebook (ERG). The yellow section ...