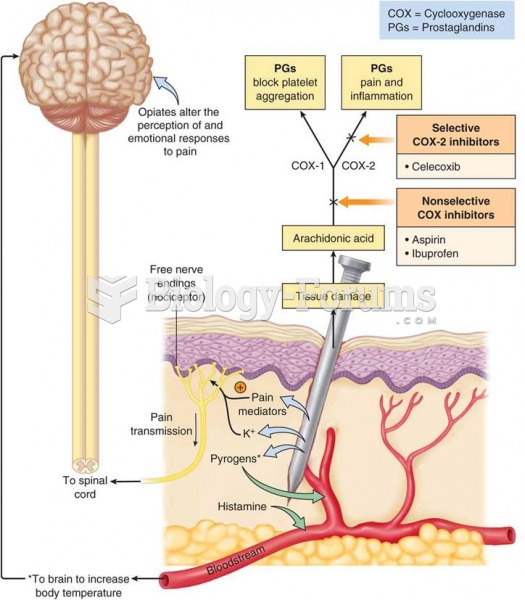
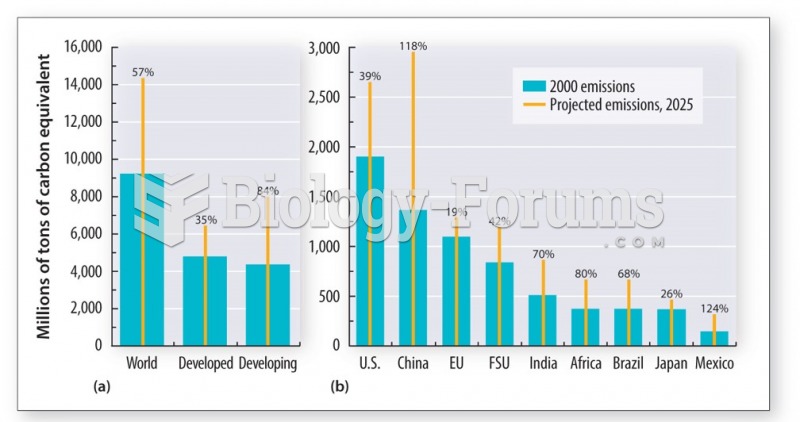
Answer to Question 1
ANSWER: When wind meets a barrier, it exerts a force upon it. If the barrier doesnt move, the wind moves around, up, and over it. As stable air flows over a ridge, it increases in speed. Thus, winds blowing over mountains tend to be stronger than winds blowing at the same level on either side. In fact, one of the greatest wind speeds ever recorded near the ground occurred at the summit of Mt. Washington, New Hampshire, elevation 1909 m (6262 ft), where the wind gusted to 201 knots (231 mi/hr) on April 12, 1934. A similar increase in wind speed occurs where air accelerates as it funnels through a narrow constriction, such as a low pass or saddle in a mountain crest.
Answer to Question 2
ANSWER: Geostationary satellites positioned above a particular location show the movement of clouds. The direction of cloud movement indicates wind direction, and the horizontal distance the cloud moves during a given time period indicates the wind speed. In addition, a specialized satellite-borne instrument called a scatterometer (a type of radar) can measure surface winds above the open ocean during all kinds of weather by observing the roughness of the sea. From the satellite, the scatterometer sends out a microwave pulse of energy that travels through the clouds, down to the sea surface. A portion of this energy is scattered (bounced) back to the satellite. The amount of energy returning to the scatterometer (called the echo) depends on the roughness of the searougher seas have a stronger echo because they scatter back more incoming energy. Since the seas roughness depends upon the strength of the wind blowing over it, the echos intensity can be translated into surface wind speed and direction. Surface wind information of this nature can be extremely valuable to the shipping industry, as well as to coastal communities. Hurricanes and other storms over the open ocean can be carefully monitored to see how their winds are changing. And incorporating sea surface wind information into computer forecast models may have the benefit of improving weather forecasts.