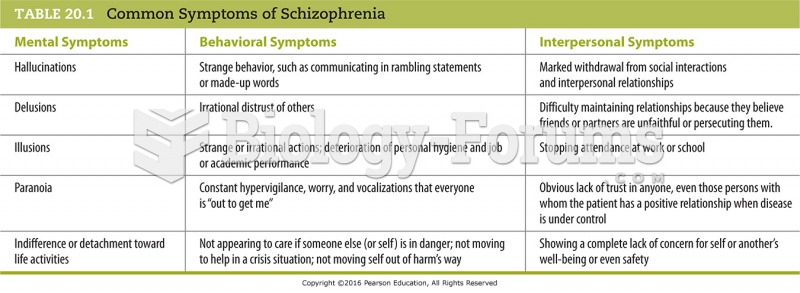
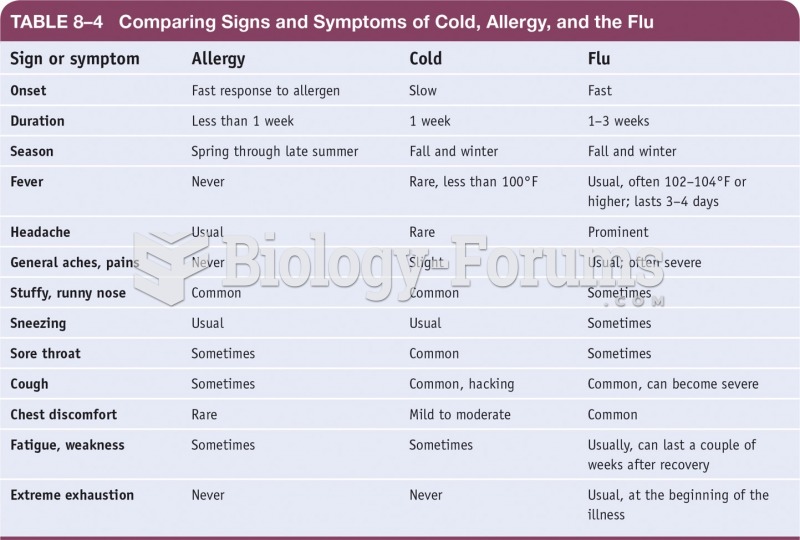
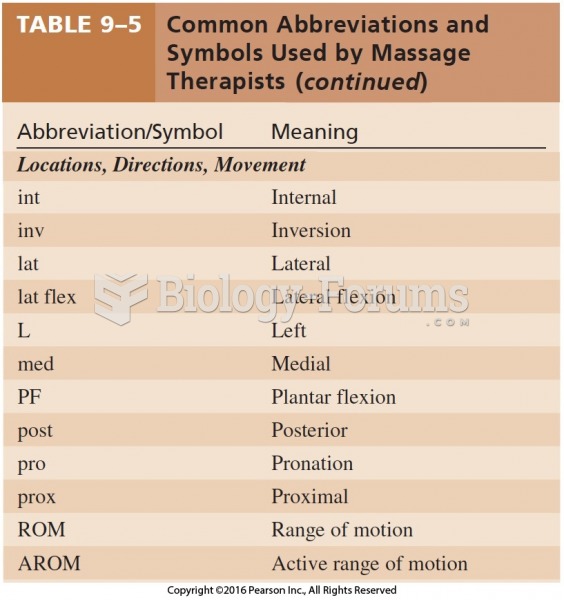
Answer to Question 1
A strong radiation inversion occurs when the air near the ground is much colder than the air higher up. Ideal conditions for a strong inversion and, hence, very low nighttime temperatures exist when the air is calm, the night is long, and the air is fairly dry and cloud-free. The ground is able to radiate its energy to outer space and thereby cool rapidly. With cloudy weather and moist air, much of the outgoing infrared energy is absorbed and radiated back to the surface, regarding the rate of cooling. Also, on humid nights, condensation in the form of fog or dew will release latent heat, which warms the air. So, radiation inversion can occur on any night. But during long winter nights, when the air is still, cloud-free, and relatively dry, these inversions can occur on any night, then, it is common to experience below-freezing temperatures near the ground, and air more than 10F warmer at your waist.
Answer to Question 2
Tropical cyclones, called hurricanes, are similar to middle-latitude cyclonic storms in that, at the surface, both have central cores of low pressure and winds that spiral counterclockwise (in the Northern Hemisphere) about their respective centers. However, there are many differences between these two storm systems. A hurricane derives its energy from the warm water and the latent heat of condensation, whereas a mid-latitude storm derives its energy from horizontal temperature contrasts. The vertical structure of a hurricane is such that its central column of air is warm from the surface upward (i.e., they are warm-core lows). A hurricane weakens with height. Mid-latitude cyclones, however, are cold-core lows that usually intensify with increasing height. A hurricane usually contains an eye where the air is sinking, while mid-latitude cyclones are characterized by centers of rising air. Hurricane winds are strongest near the surface, whereas the strongest winds of the mid-latitude cyclones are found aloft in the jet stream. Even though hurricanes weaken rapidly as they move inland, their circulation may draw in air with contrasting properties and if the hurricane links with an upper-level trough, it may actually become a mid-latitude cyclone.