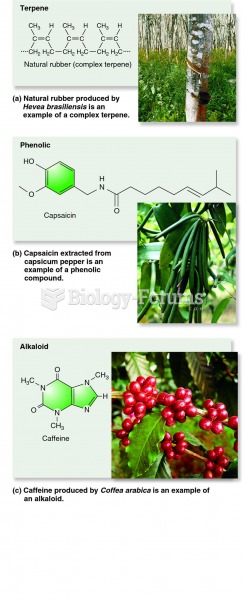
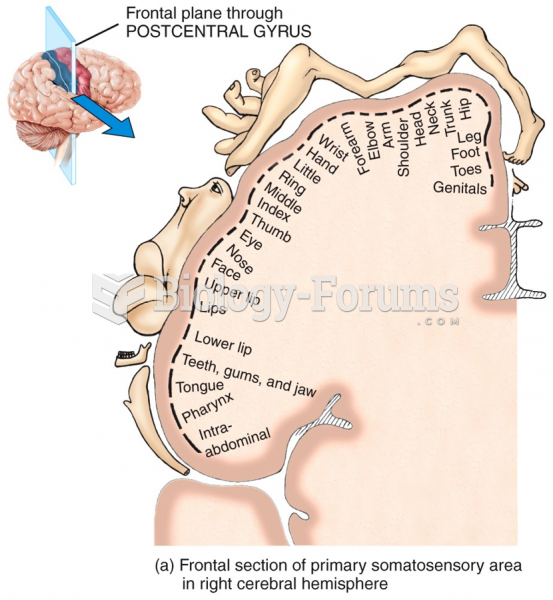
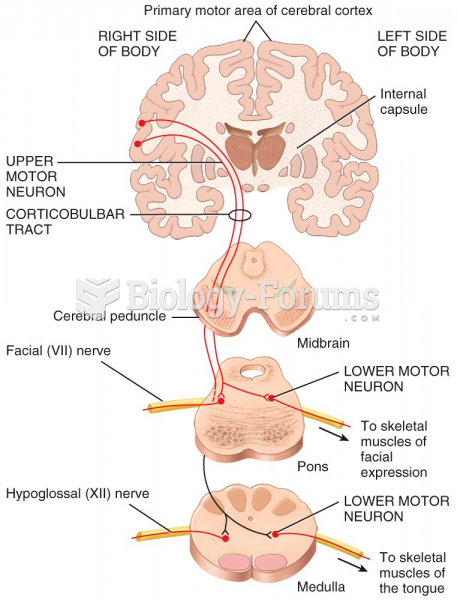
Answer to Question 1
Answer: Primary pollutants, are emitted directly into the atmosphere. Secondary pollutants do not go directly into the atmosphere but result from one or more chemical transformations.
Answer to Question 2
Answer: Particulates (also called aerosols) are solid and liquid materials in the air that are of natural or anthropogenic (human- made) origin. Some of the particulates are primary pollutants put directly into the atmosphere, whereas others are secondary pollutants formed by the transformation of preexisting gases or from the growth of smaller particulates into larger ones by coagulation. Particulates introduced directly into the air can originate from natural fires, volcanic eruptions, the ejection of salt crystals by breaking ocean waves, and by the entrainment of pollen by wind. Several different processes remove particulates from the air. Gravitational settling, the process wherein particulates fall from the air (even if very slowly), effectively removes larger particulates. The smaller ones are less susceptible to this process because even very small eddies can keep them in suspension. Precipitation, on the other hand, removes both large and small particulates in two ways. First, the particulates that served as condensation nuclei in clouds are removed when the droplets that they are part of fall as rain or snow. Other particulates are removed by scavenging, the process in which falling droplets and crystals collide with particulates in their path. Upon collision, the precipitation incorporates the particulate and carries it to the surface. The scavenging of particulates largely explains why the air is so much cleaner and visibility is enhanced after a rain shower. A certain class of particulatesthose smaller than 10 m in diameter (called PM10)most readily enters the lungs and brings about the most serious tissue damage. A large body of research analyzing the effects of particulates has shown that a more specific class of particulates those smaller than 2.5 m (called PM2.5)also presents serious health problems.