|
|
|
Although the Roman numeral for the number 4 has always been taught to have been "IV," according to historians, the ancient Romans probably used "IIII" most of the time. This is partially backed up by the fact that early grandfather clocks displayed IIII for the number 4 instead of IV. Early clockmakers apparently thought that the IIII balanced out the VIII (used for the number 8) on the clock face and that it just looked better.
Green tea is able to stop the scent of garlic or onion from causing bad breath.
Between 1999 and 2012, American adults with high total cholesterol decreased from 18.3% to 12.9%
Certain chemicals, after ingestion, can be converted by the body into cyanide. Most of these chemicals have been removed from the market, but some old nail polish remover, solvents, and plastics manufacturing solutions can contain these substances.
Many of the drugs used by neuroscientists are derived from toxic plants and venomous animals (such as snakes, spiders, snails, and puffer fish).
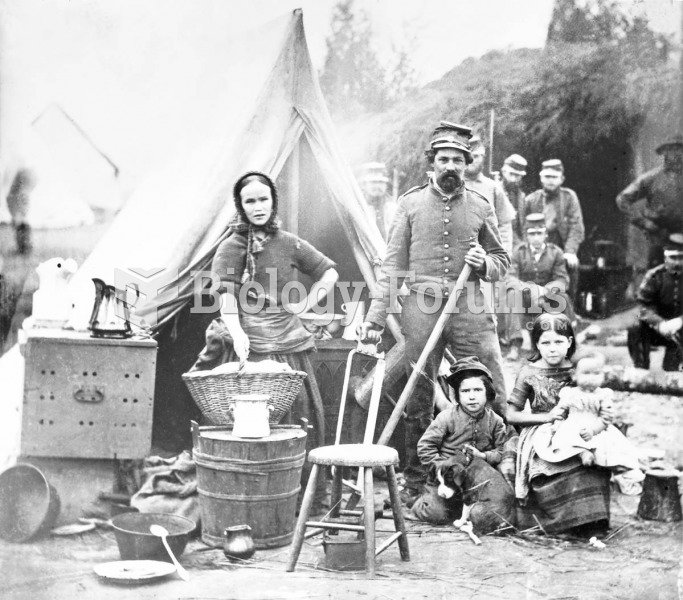 The family of a soldier in the 31st Philadelphia Infantry camps near Washington, DC. Although both a
The family of a soldier in the 31st Philadelphia Infantry camps near Washington, DC. Although both a
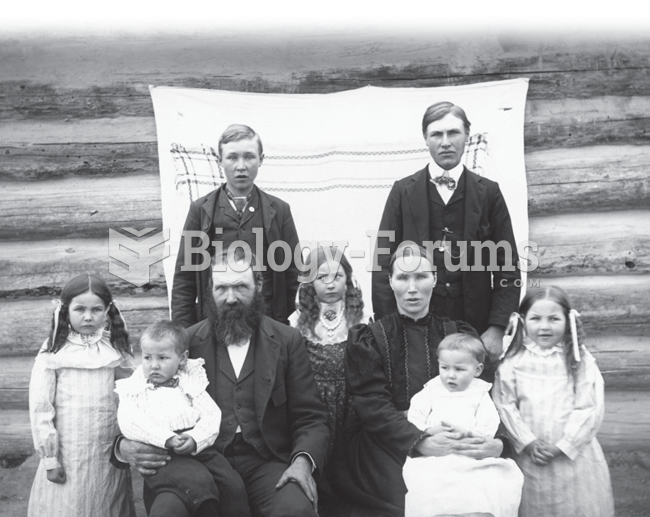 Large families on U.S. farms used to be common. Children helped plant and harvest crops, take care ...
Large families on U.S. farms used to be common. Children helped plant and harvest crops, take care ...