|
|
|
Certain rare plants containing cyanide include apricot pits and a type of potato called cassava. Fortunately, only chronic or massive ingestion of any of these plants can lead to serious poisoning.
Cyanide works by making the human body unable to use oxygen.
Walt Disney helped combat malaria by making an animated film in 1943 called The Winged Scourge. This short film starred the seven dwarfs and taught children that mosquitos transmit malaria, which is a very bad disease. It advocated the killing of mosquitos to stop the disease.
In 2006, a generic antinausea drug named ondansetron was approved. It is used to stop nausea and vomiting associated with surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.
Hip fractures are the most serious consequences of osteoporosis. The incidence of hip fractures increases with each decade among patients in their 60s to patients in their 90s for both women and men of all populations. Men and women older than 80 years of age show the highest incidence of hip fractures.
 Photograph of the flea that transmits Yersinia pestis to cause bubonic plague, called the oriental r
Photograph of the flea that transmits Yersinia pestis to cause bubonic plague, called the oriental r
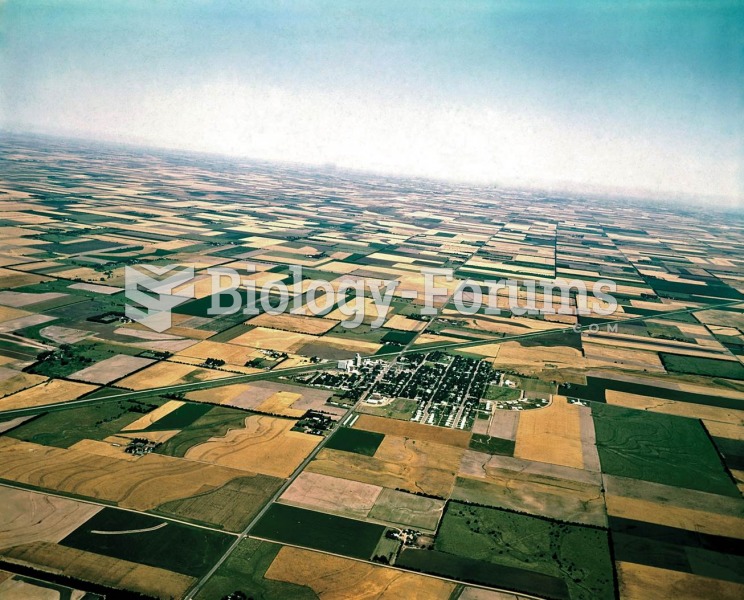 The Land Ordinance of 1785 called for surveying and dividing the Western Territories into square mil
The Land Ordinance of 1785 called for surveying and dividing the Western Territories into square mil