Answer to Question 1
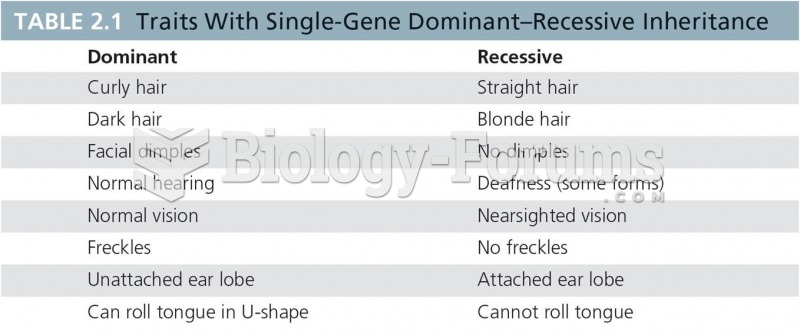
Basic sorting takes place when waste is collected, either through curbside collection or by town recycling stations (sites to which townspeople can bring wastes to be recycled). The waste is then trucked to the MRF and handled on three tracks: one for metal cans and glass containers, another for paper products, and a third for plastics. The materials are moved through the facility by escalators and conveyor belts, tended by workers who inspect and sort further. The objective of the process is to prepare materials for the recycled-goods market. Glass is sorted by color, cleaned, crushed into small pebbles, and then shipped to glass companies, where it replaces the raw materials that go into glass manufacturesand and soda ashand saves substantially on energy costs. Cans are sorted, flattened, and sent either to de-tinning plants or to aluminum-processing facilities. Paper is sorted, baled, and sent to reprocessing mills. Plastics are sorted into four categories, depending on their color and type of polymer, and then sold. The facility's advantages are its economy of scale and its ability to produce a high-quality end product for the recycled materials market.
Less common than conventional MRFs, the mixed-waste processing facility receives MSW just as if it were going to a landfill or a WTE facility. The waste is loaded on a conveyer and is sorted for recovery of recyclable materials before being landfilled or combusted.
Taking advantage of the fact that MSW has a high organic content, a few regional facilities compost the MSW after removing large items and metals. Often, they will mix treated sewage sludge with the MSW (called co-composting), which provides a rich source of bacteria and nutrients.
Single-stream recovery involves the collection of all types of recycled materials (paper, glass, metal) in a single container. The materials are then sorted later at the MRE. This has the benefit of helping the consumer to reduce the time required to recycle and also decreases the time that collectors spend collecting the recycled materials. The time is spent later, however, at the sorting facility.
Answer to Question 2
Soil texture can be differentiated by the proportion of sand, silt, and clay. If sand predominates, the soil is called sandy and the particle size ranges from 2.0 to 0.02 mm. If silt predominates, then the soil is called silty and the particles range from 0.02 to 0.002 mm. If clay predominates, the soil is called clayey and the particles are less than 0.002 mm. If the soil is roughly 40 sand, 40 silt, and 20 clay, the soil is called loam. The three properties are larger particles have larger spaces separating them than smaller particles have, smaller particles have more surface area relative to their volume than larger particles have, and nutrient ions and water molecules tend to cling to surfaces.