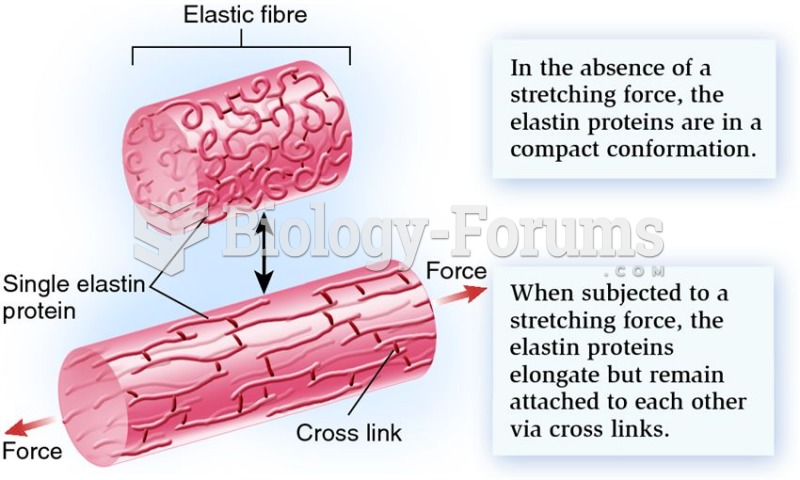
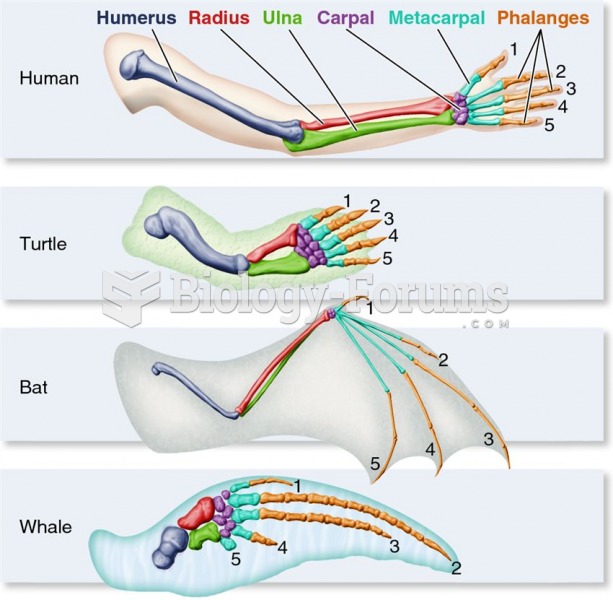
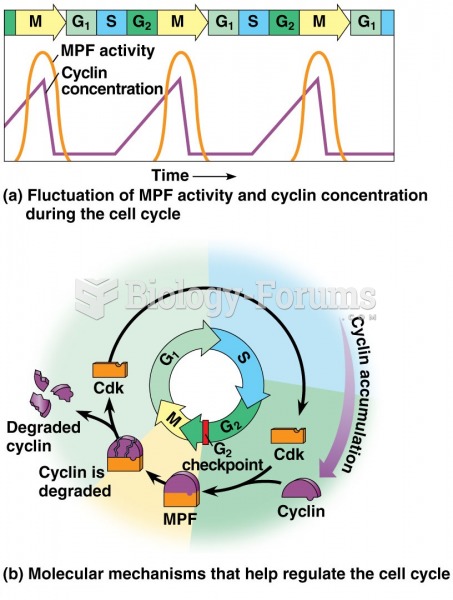
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
If you could remove all of your skin, it would weigh up to 5 pounds.
Did you know?
According to the FDA, adverse drug events harmed or killed approximately 1,200,000 people in the United States in the year 2015.
Did you know?
Acetaminophen (Tylenol) in overdose can seriously damage the liver. It should never be taken by people who use alcohol heavily; it can result in severe liver damage and even a condition requiring a liver transplant.
Did you know?
The calories found in one piece of cherry cheesecake could light a 60-watt light bulb for 1.5 hours.
Did you know?
Excessive alcohol use costs the country approximately $235 billion every year.