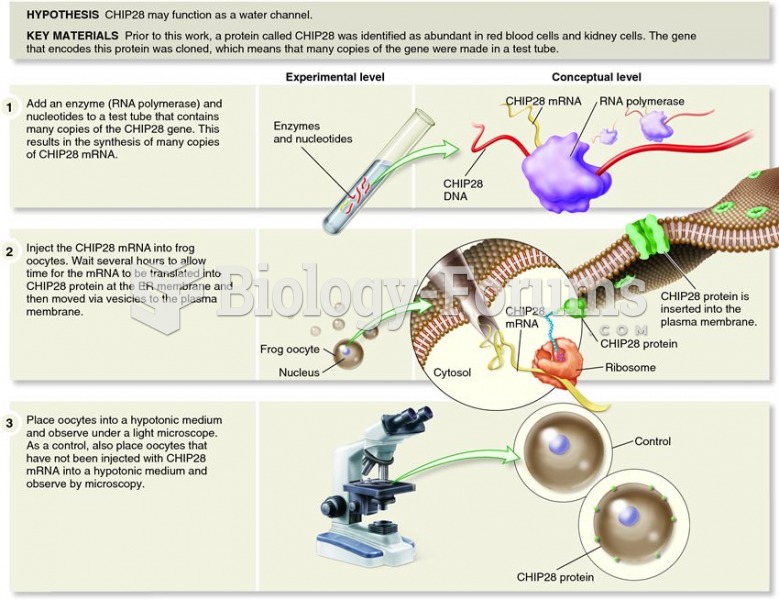
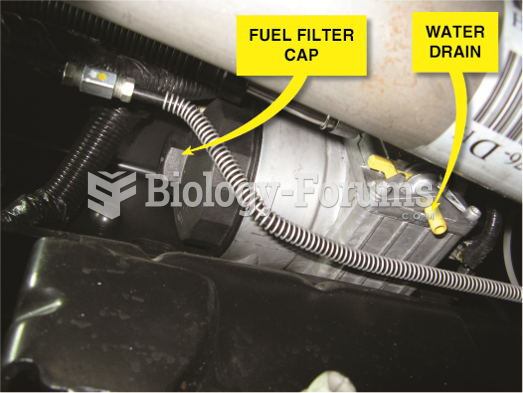
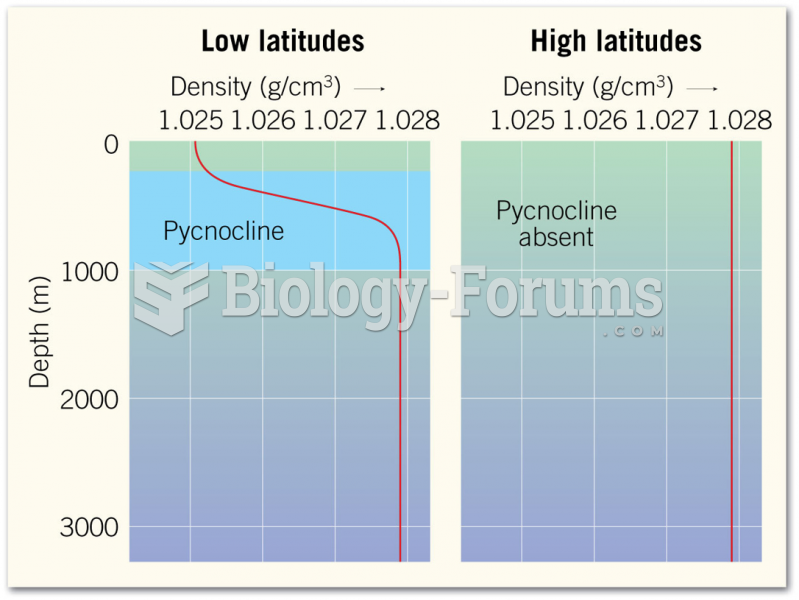
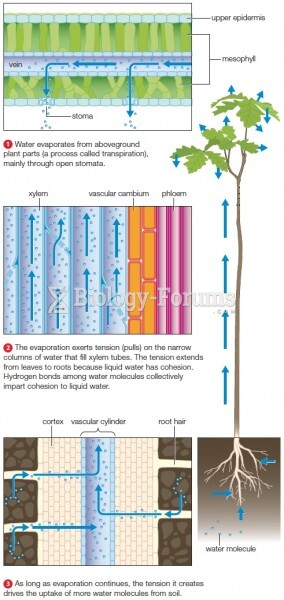
|
|
|
When blood is exposed to air, it clots. Heparin allows the blood to come in direct contact with air without clotting.
Vaccines cause herd immunity. If the majority of people in a community have been vaccinated against a disease, an unvaccinated person is less likely to get the disease since others are less likely to become sick from it and spread the disease.
More than 50% of American adults have oral herpes, which is commonly known as "cold sores" or "fever blisters." The herpes virus can be active on the skin surface without showing any signs or causing any symptoms.
Most fungi that pathogenically affect humans live in soil. If a person is not healthy, has an open wound, or is immunocompromised, a fungal infection can be very aggressive.
According to the FDA, adverse drug events harmed or killed approximately 1,200,000 people in the United States in the year 2015.