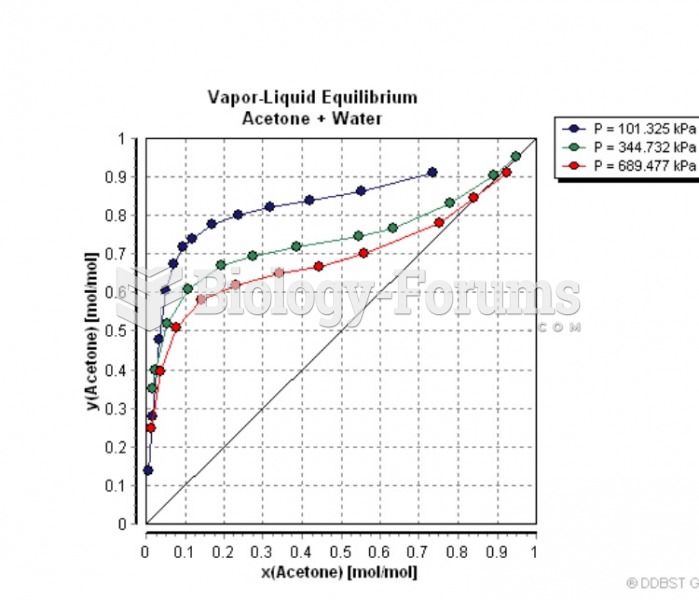
|
|
|
Most strokes are caused when blood clots move to a blood vessel in the brain and block blood flow to that area. Thrombolytic therapy can be used to dissolve the clot quickly. If given within 3 hours of the first stroke symptoms, this therapy can help limit stroke damage and disability.
Cytomegalovirus affects nearly the same amount of newborns every year as Down syndrome.
Cyanide works by making the human body unable to use oxygen.
The average office desk has 400 times more bacteria on it than a toilet.
Always store hazardous household chemicals in their original containers out of reach of children. These include bleach, paint, strippers and products containing turpentine, garden chemicals, oven cleaners, fondue fuels, nail polish, and nail polish remover.