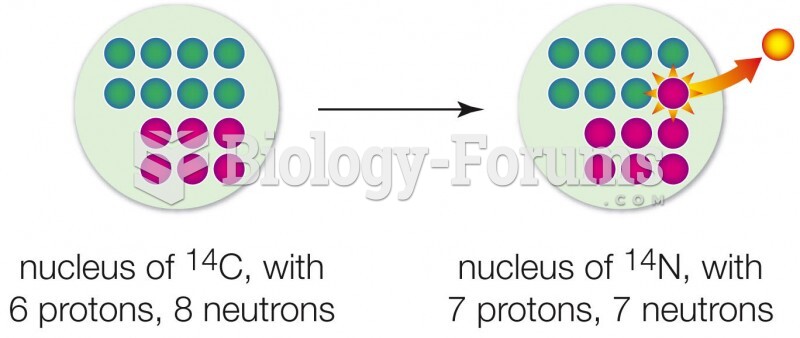
|
|
|
The oldest recorded age was 122. Madame Jeanne Calment was born in France in 1875 and died in 1997. She was a vegetarian and loved olive oil, port wine, and chocolate.
In 1886, William Bates reported on the discovery of a substance produced by the adrenal gland that turned out to be epinephrine (adrenaline). In 1904, this drug was first artificially synthesized by Friedrich Stolz.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has released reports detailing the deaths of infants (younger than 1 year of age) who died after being given cold and cough medications. This underscores the importance of educating parents that children younger than 2 years of age should never be given over-the-counter cold and cough medications without consulting their physicians.
Hypertension is a silent killer because it is deadly and has no significant early symptoms. The danger from hypertension is the extra load on the heart, which can lead to hypertensive heart disease and kidney damage. This occurs without any major symptoms until the high blood pressure becomes extreme. Regular blood pressure checks are an important method of catching hypertension before it can kill you.
Patients should never assume they are being given the appropriate drugs. They should make sure they know which drugs are being prescribed, and always double-check that the drugs received match the prescription.