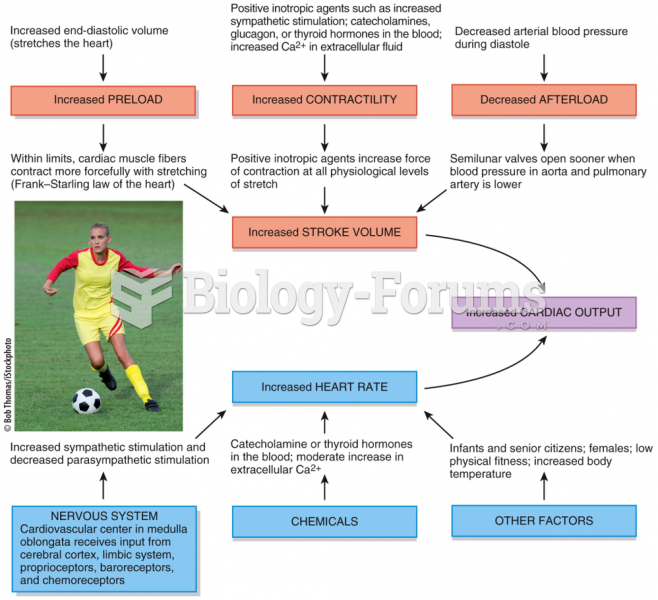
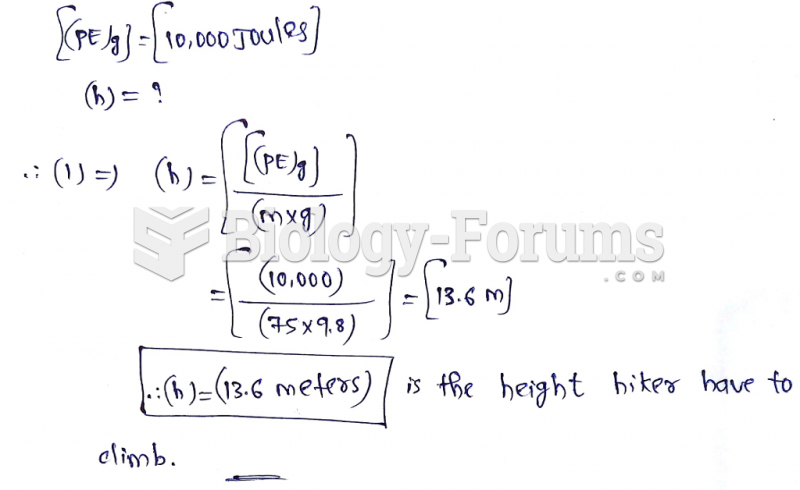
|
|
|
Immunoglobulin injections may give short-term protection against, or reduce severity of certain diseases. They help people who have an inherited problem making their own antibodies, or those who are having certain types of cancer treatments.
No drugs are available to relieve parathyroid disease. Parathyroid disease is caused by a parathyroid tumor, and it needs to be removed by surgery.
Complications of influenza include: bacterial pneumonia, ear and sinus infections, dehydration, and worsening of chronic conditions such as asthma, congestive heart failure, or diabetes.
Patients who cannot swallow may receive nutrition via a parenteral route—usually, a catheter is inserted through the chest into a large vein going into the heart.
Though Candida and Aspergillus species are the most common fungal pathogens causing invasive fungal disease in the immunocompromised, infections due to previously uncommon hyaline and dematiaceous filamentous fungi are occurring more often today. Rare fungal infections, once accurately diagnosed, may require surgical debridement, immunotherapy, and newer antifungals used singly or in combination with older antifungals, on a case-by-case basis.