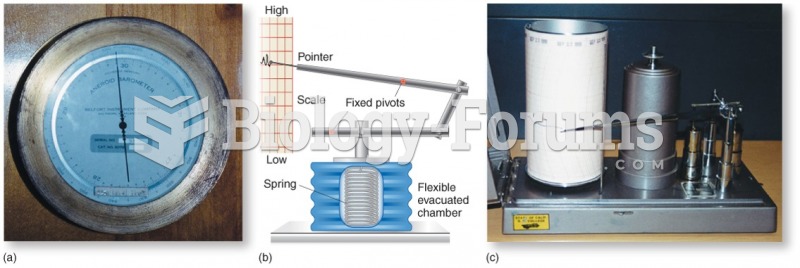
|
|
|
Though “Krazy Glue” or “Super Glue” has the ability to seal small wounds, it is not recommended for this purpose since it contains many substances that should not enter the body through the skin, and may be harmful.
According to the Migraine Research Foundation, migraines are the third most prevalent illness in the world. Women are most affected (18%), followed by children of both sexes (10%), and men (6%).
The use of salicylates dates back 2,500 years to Hippocrates’s recommendation of willow bark (from which a salicylate is derived) as an aid to the pains of childbirth. However, overdosage of salicylates can harm body fluids, electrolytes, the CNS, the GI tract, the ears, the lungs, the blood, the liver, and the kidneys and cause coma or death.
Hyperthyroidism leads to an increased rate of metabolism and affects about 1% of women but only 0.1% of men. For most people, this increased metabolic rate causes the thyroid gland to become enlarged (known as a goiter).
A good example of polar molecules can be understood when trying to make a cake. If water and oil are required, they will not mix together. If you put them into a measuring cup, the oil will rise to the top while the water remains on the bottom.