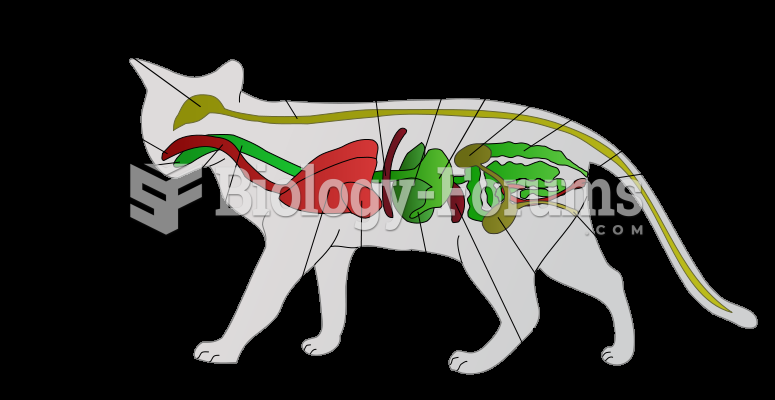
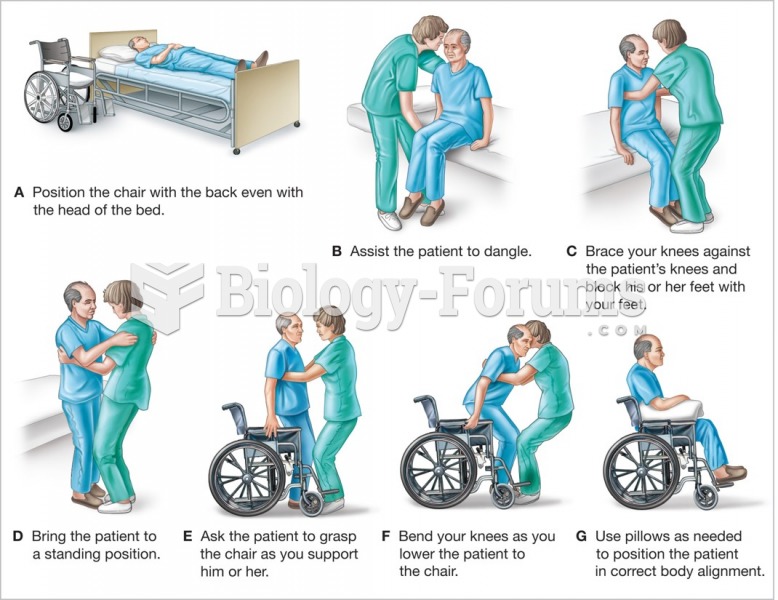
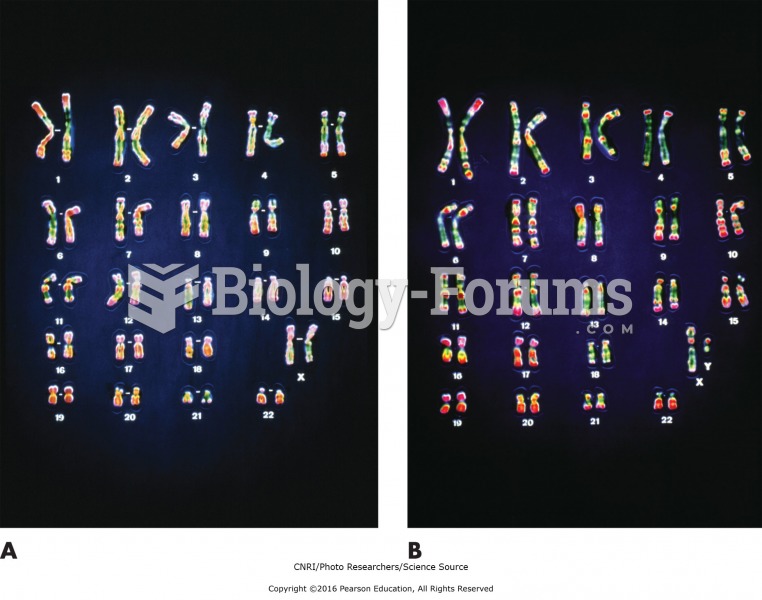
|
|
|
Did you know?
The U.S. Pharmacopeia Medication Errors Reporting Program states that approximately 50% of all medication errors involve insulin.
Did you know?
HIV testing reach is still limited. An estimated 40% of people with HIV (more than 14 million) remain undiagnosed and do not know their infection status.
Did you know?
There are more sensory neurons in the tongue than in any other part of the body.
Did you know?
Despite claims by manufacturers, the supplement known as Ginkgo biloba was shown in a study of more than 3,000 participants to be ineffective in reducing development of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease in older people.
Did you know?
Alcohol acts as a diuretic. Eight ounces of water is needed to metabolize just 1 ounce of alcohol.