This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
This year, an estimated 1.4 million Americans will have a new or recurrent heart attack.
Did you know?
More than 150,000 Americans killed by cardiovascular disease are younger than the age of 65 years.
Did you know?
Most childhood vaccines are 90–99% effective in preventing disease. Side effects are rarely serious.
Did you know?
Warfarin was developed as a consequence of the study of a strange bleeding disorder that suddenly occurred in cattle on the northern prairies of the United States in the early 1900s.
Did you know?
Russia has the highest death rate from cardiovascular disease followed by the Ukraine, Romania, Hungary, and Poland.
 Muskox populations remain in the Arctic all year, though they migrate to higher elevations in the wi
Muskox populations remain in the Arctic all year, though they migrate to higher elevations in the wi
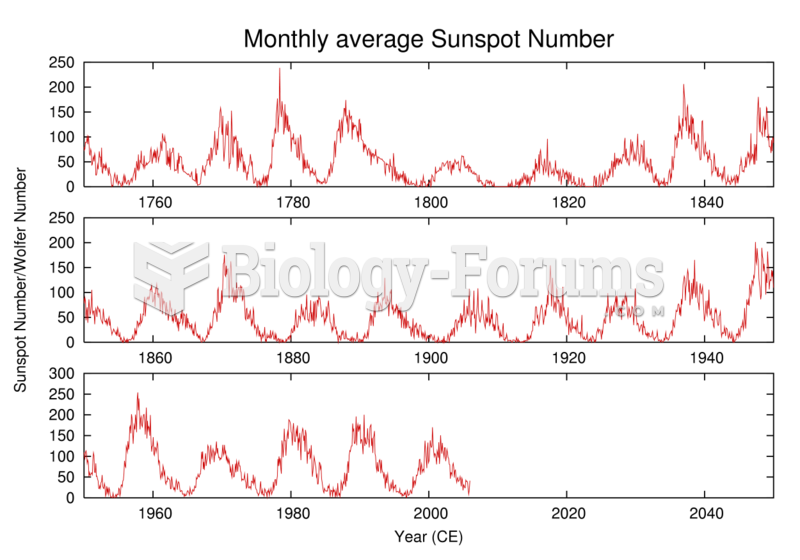 History of the number of observed sunspots during the last 250 years, which shows the ~11-year solar
History of the number of observed sunspots during the last 250 years, which shows the ~11-year solar
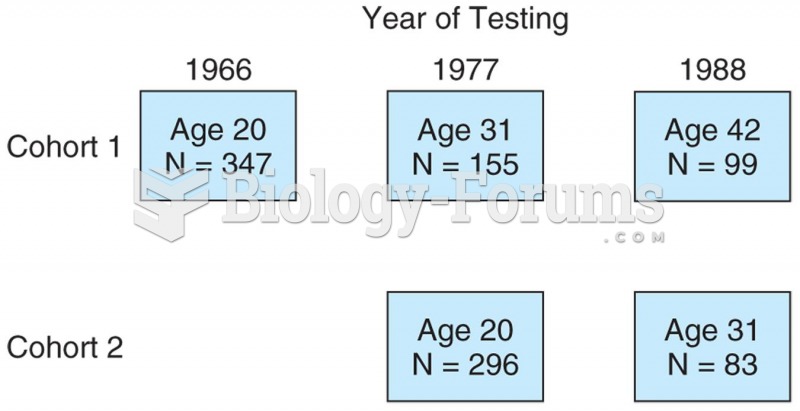 Model of a sequential study in which two cohorts were followed beginning at age 20. One cohort was f
Model of a sequential study in which two cohorts were followed beginning at age 20. One cohort was f