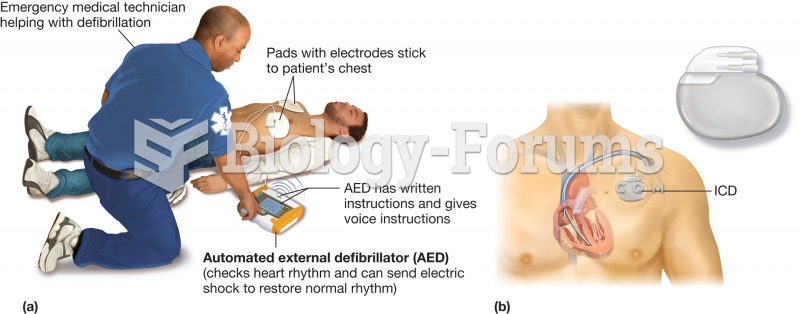
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Throughout history, plants containing cardiac steroids have been used as heart drugs and as poisons (e.g., in arrows used in combat), emetics, and diuretics.
Did you know?
Intradermal injections are somewhat difficult to correctly administer because the skin layers are so thin that it is easy to accidentally punch through to the deeper subcutaneous layer.
Did you know?
About 600,000 particles of skin are shed every hour by each human. If you live to age 70 years, you have shed 105 pounds of dead skin.
Did you know?
Carbamazepine can interfere with the results of home pregnancy tests. If you are taking carbamazepine, do not try to test for pregnancy at home.
Did you know?
The horizontal fraction bar was introduced by the Arabs.