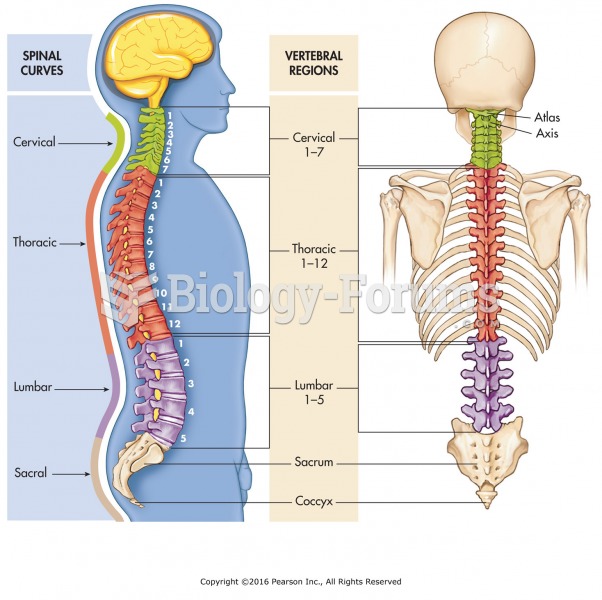
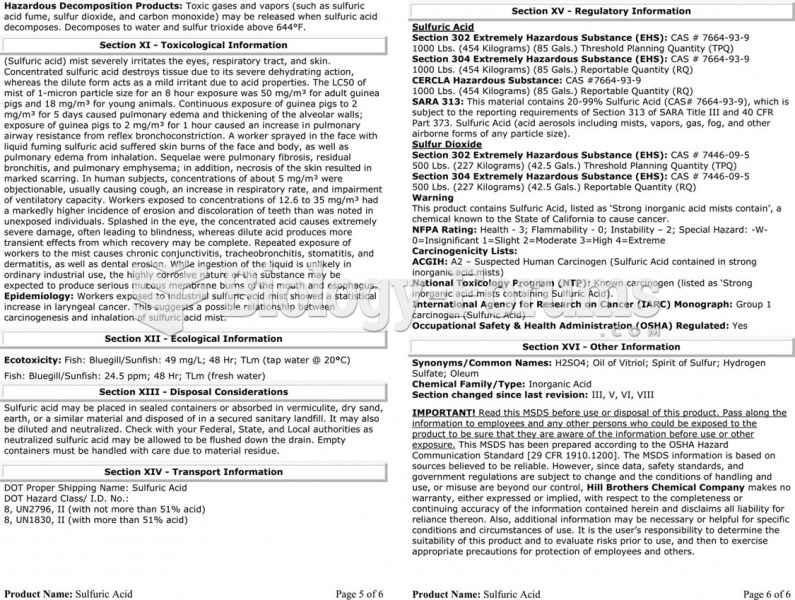
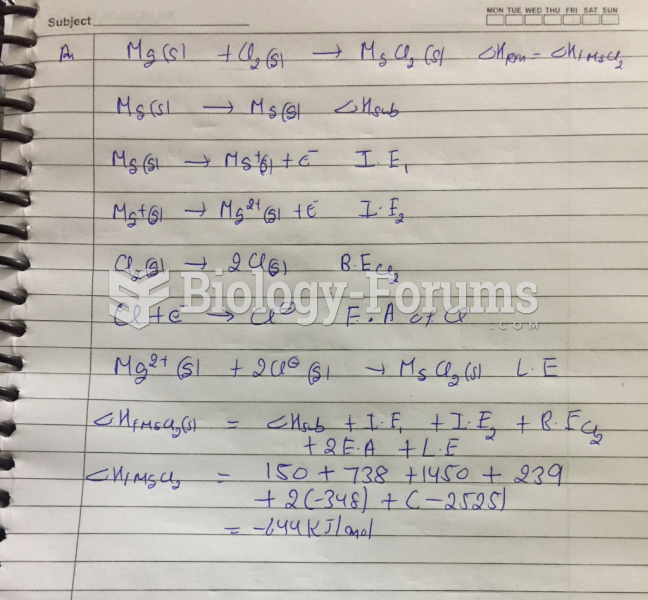
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
HIV testing reach is still limited. An estimated 40% of people with HIV (more than 14 million) remain undiagnosed and do not know their infection status.
Did you know?
Patients who have been on total parenteral nutrition for more than a few days may need to have foods gradually reintroduced to give the digestive tract time to start working again.
Did you know?
Today, nearly 8 out of 10 pregnant women living with HIV (about 1.1 million), receive antiretrovirals.
Did you know?
Blood is approximately twice as thick as water because of the cells and other components found in it.
Did you know?
Pregnant women usually experience a heightened sense of smell beginning late in the first trimester. Some experts call this the body's way of protecting a pregnant woman from foods that are unsafe for the fetus.
 Examining the survivorship curve of a Dall mountain sheep population reveals information on the caus
Examining the survivorship curve of a Dall mountain sheep population reveals information on the caus
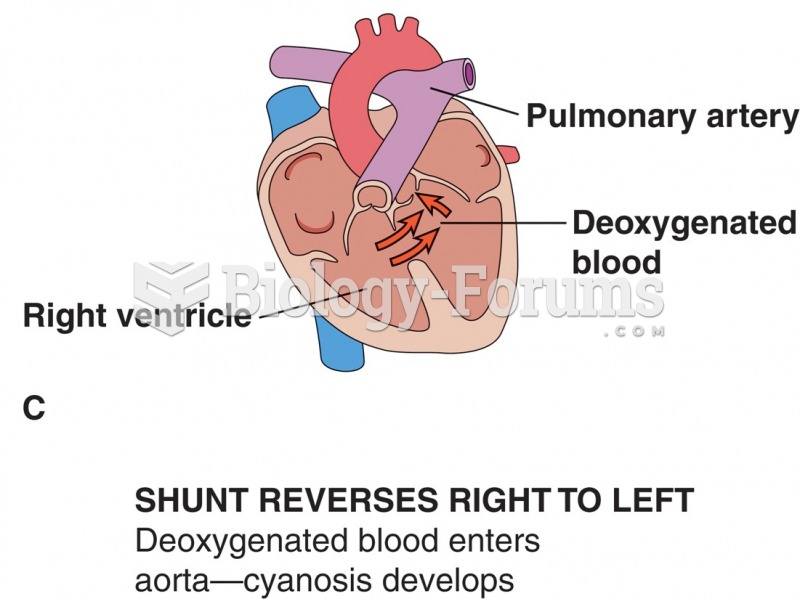 Effects of septal defects: (A) normal shunt; no cyanosis; (B) increased pressure in right ventricle; ...
Effects of septal defects: (A) normal shunt; no cyanosis; (B) increased pressure in right ventricle; ...