|
|
|
The longest a person has survived after a heart transplant is 24 years.
People who have myopia, or nearsightedness, are not able to see objects at a distance but only up close. It occurs when the cornea is either curved too steeply, the eye is too long, or both. This condition is progressive and worsens with time. More than 100 million people in the United States are nearsighted, but only 20% of those are born with the condition. Diet, eye exercise, drug therapy, and corrective lenses can all help manage nearsightedness.
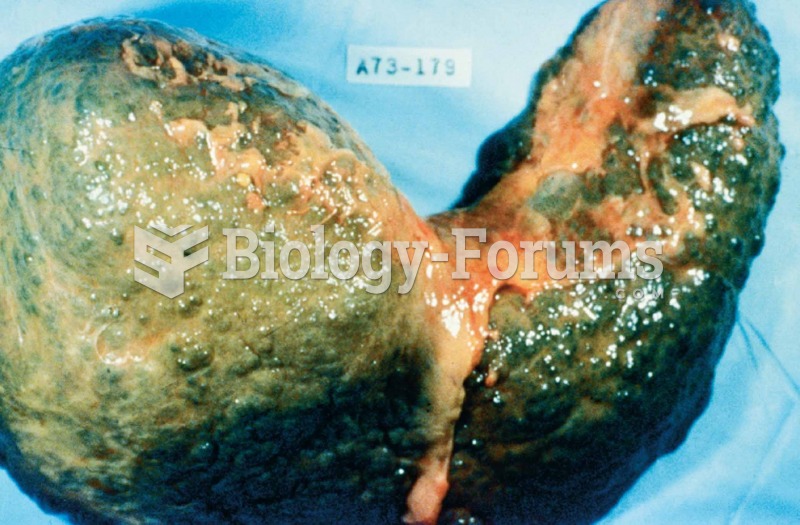
In most cases, kidneys can recover from almost complete loss of function, such as in acute kidney (renal) failure.
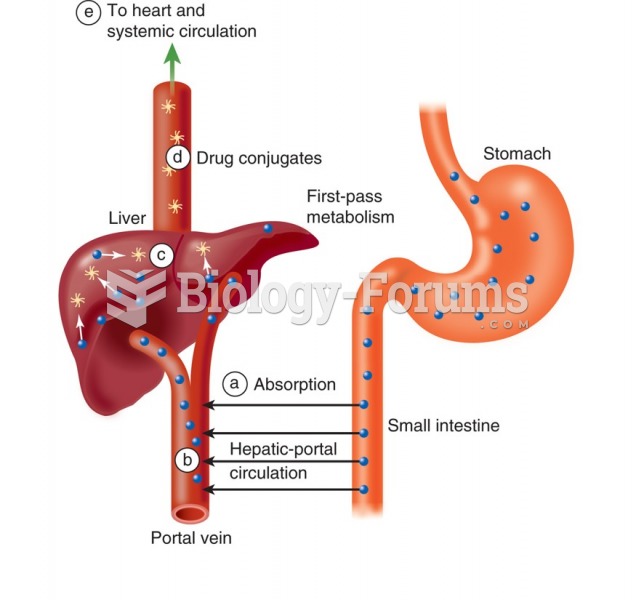
About 100 new prescription or over-the-counter drugs come into the U.S. market every year.
Drugs are in development that may cure asthma and hay fever once and for all. They target leukotrienes, which are known to cause tightening of the air passages in the lungs and increase mucus productions in nasal passages.