|
|
|
According to research, pregnant women tend to eat more if carrying a baby boy. Male fetuses may secrete a chemical that stimulates their mothers to step up her energy intake.
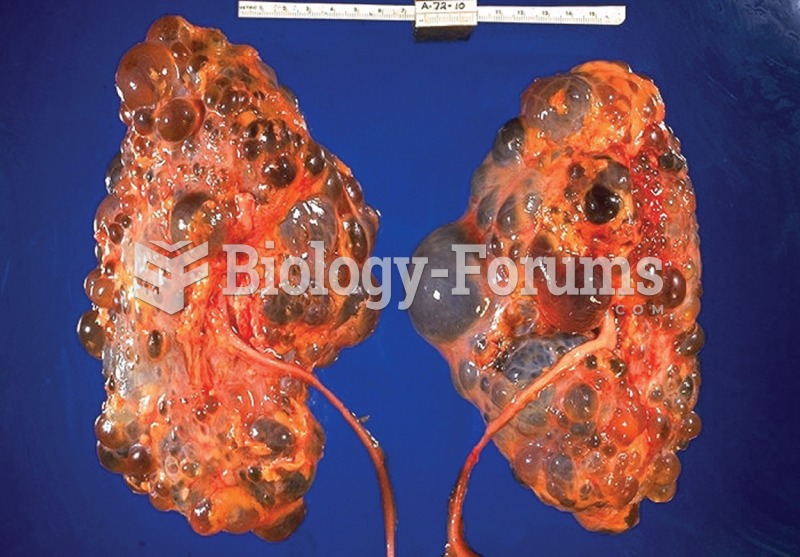
Normal urine is sterile. It contains fluids, salts, and waste products. It is free of bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
It is believed that humans initially contracted crabs from gorillas about 3 million years ago from either sleeping in gorilla nests or eating the apes.
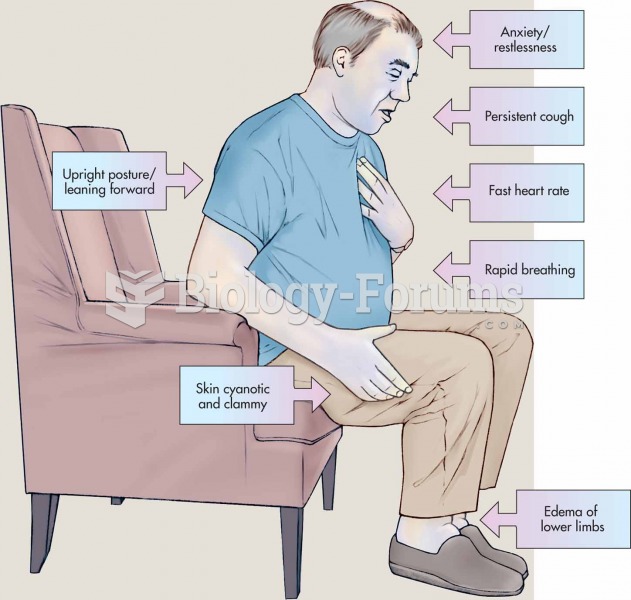
Amphetamine poisoning can cause intravascular coagulation, circulatory collapse, rhabdomyolysis, ischemic colitis, acute psychosis, hyperthermia, respiratory distress syndrome, and pericarditis.
Amphetamine poisoning can cause intravascular coagulation, circulatory collapse, rhabdomyolysis, ischemic colitis, acute psychosis, hyperthermia, respiratory distress syndrome, and pericarditis.