|
|
|
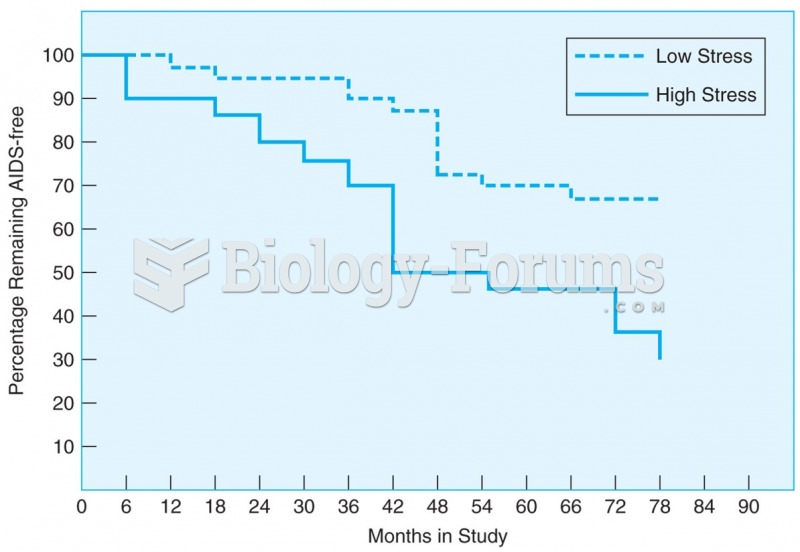
Congestive heart failure is a serious disorder that carries a reduced life expectancy. Heart failure is usually a chronic illness, and it may worsen with infection or other physical stressors.
Bisphosphonates were first developed in the nineteenth century. They were first investigated for use in disorders of bone metabolism in the 1960s. They are now used clinically for the treatment of osteoporosis, Paget's disease, bone metastasis, multiple myeloma, and other conditions that feature bone fragility.
Adults are resistant to the bacterium that causes Botulism. These bacteria thrive in honey – therefore, honey should never be given to infants since their immune systems are not yet resistant.
Urine turns bright yellow if larger than normal amounts of certain substances are consumed; one of these substances is asparagus.
The first-known contraceptive was crocodile dung, used in Egypt in 2000 BC. Condoms were also reportedly used, made of animal bladders or intestines.