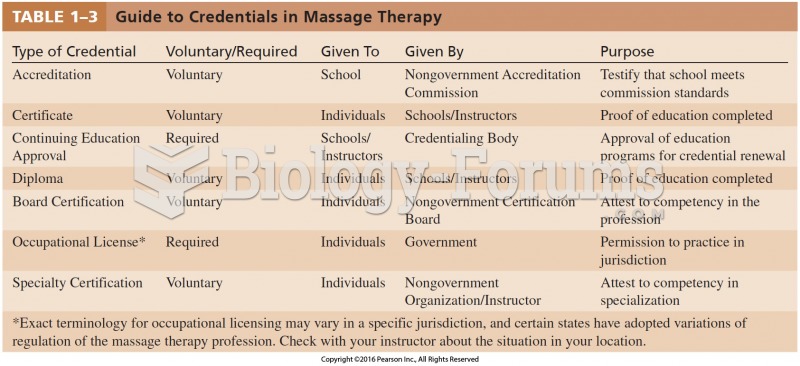
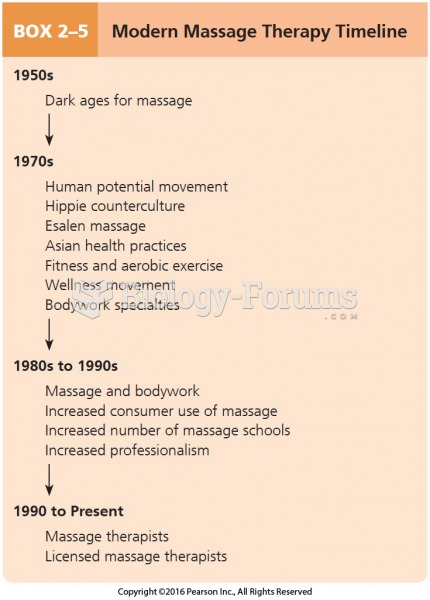
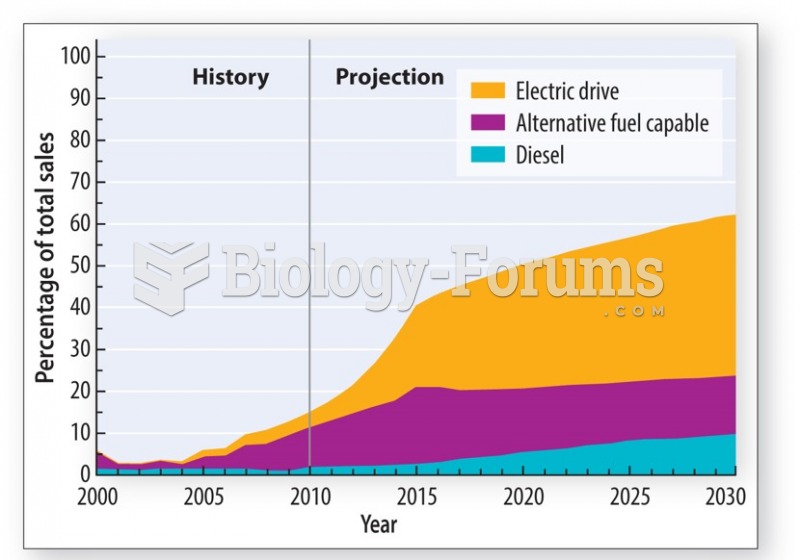
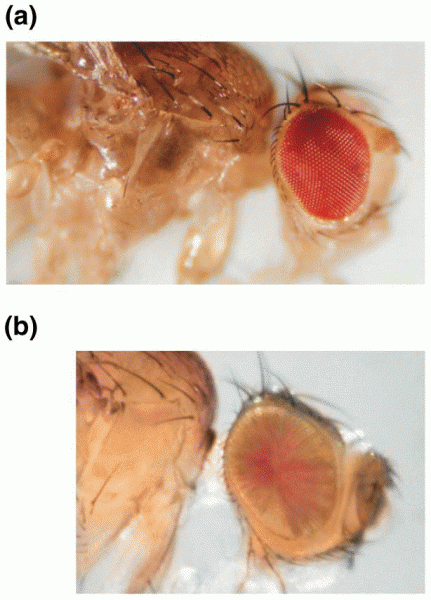
|
|
|
Children with strabismus (crossed eyes) can be treated. They are not able to outgrow this condition on their own, but with help, it can be more easily corrected at a younger age. It is important for infants to have eye examinations as early as possible in their development and then another at age 2 years.
There can actually be a 25-hour time difference between certain locations in the world. The International Date Line passes between the islands of Samoa and American Samoa. It is not a straight line, but "zig-zags" around various island chains. Therefore, Samoa and nearby islands have one date, while American Samoa and nearby islands are one day behind. Daylight saving time is used in some islands, but not in others—further shifting the hours out of sync with natural time.
To prove that stomach ulcers were caused by bacteria and not by stress, a researcher consumed an entire laboratory beaker full of bacterial culture. After this, he did indeed develop stomach ulcers, and won the Nobel Prize for his discovery.
It is believed that humans initially contracted crabs from gorillas about 3 million years ago from either sleeping in gorilla nests or eating the apes.
There are actually 60 minerals, 16 vitamins, 12 essential amino acids, and three essential fatty acids that your body needs every day.