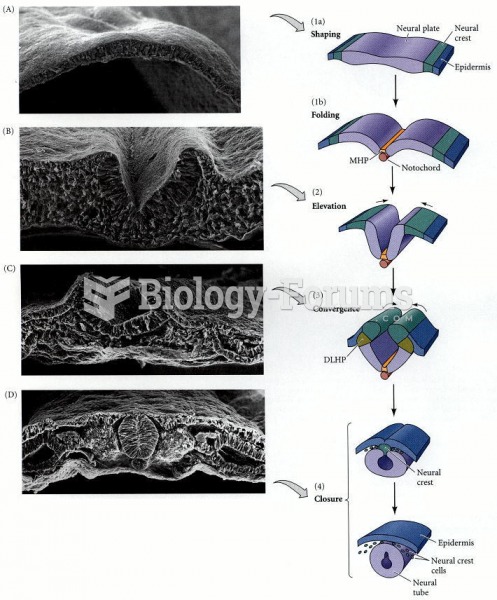
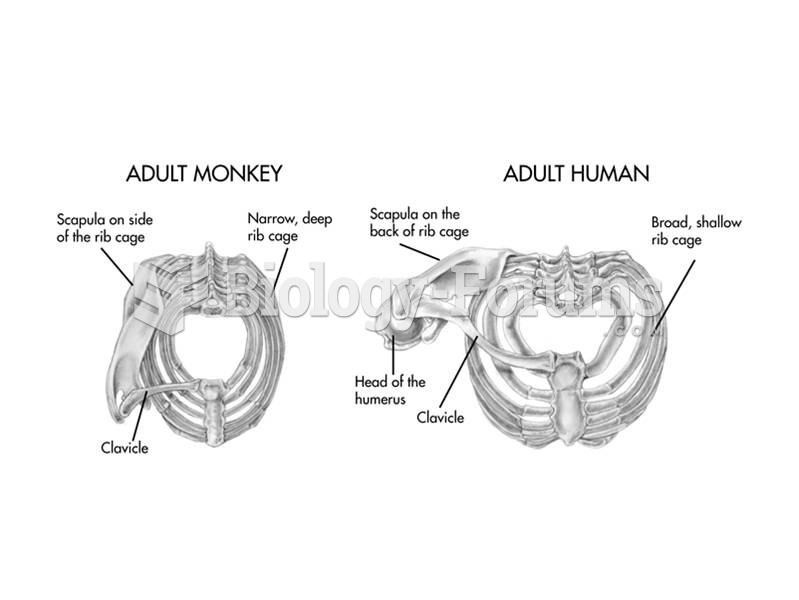
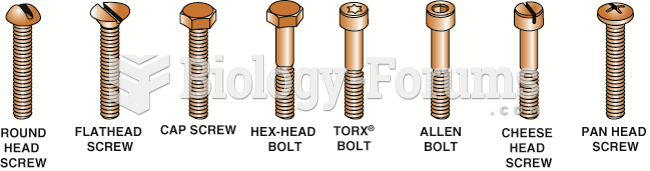
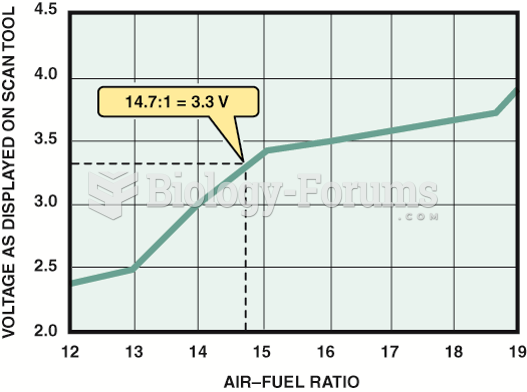
|
|
|
When taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors, people should avoid a variety of foods, which include alcoholic beverages, bean curd, broad (fava) bean pods, cheese, fish, ginseng, protein extracts, meat, sauerkraut, shrimp paste, soups, and yeast.
In the United States, an estimated 50 million unnecessary antibiotics are prescribed for viral respiratory infections.
Chronic marijuana use can damage the white blood cells and reduce the immune system's ability to respond to disease by as much as 40%. Without a strong immune system, the body is vulnerable to all kinds of degenerative and infectious diseases.
In 1844, Charles Goodyear obtained the first patent for a rubber condom.
The strongest synthetic topical retinoid drug available, tazarotene, is used to treat sun-damaged skin, acne, and psoriasis.