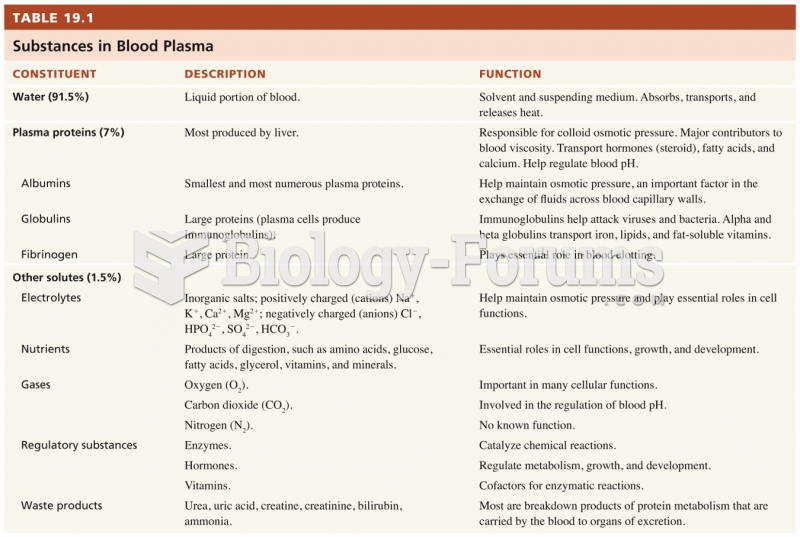
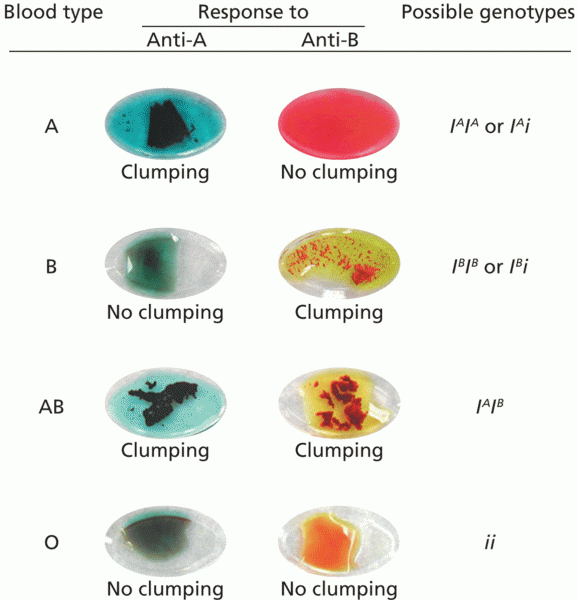
|
|
|
The people with the highest levels of LDL are Mexican American males and non-Hispanic black females.
Looking at the sun may not only cause headache and distort your vision temporarily, but it can also cause permanent eye damage. Any exposure to sunlight adds to the cumulative effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation on your eyes. UV exposure has been linked to eye disorders such as macular degeneration, solar retinitis, and corneal dystrophies.
The FDA recognizes 118 routes of administration.
About 100 new prescription or over-the-counter drugs come into the U.S. market every year.
People often find it difficult to accept the idea that bacteria can be beneficial and improve health. Lactic acid bacteria are good, and when eaten, these bacteria improve health and increase longevity. These bacteria included in foods such as yogurt.