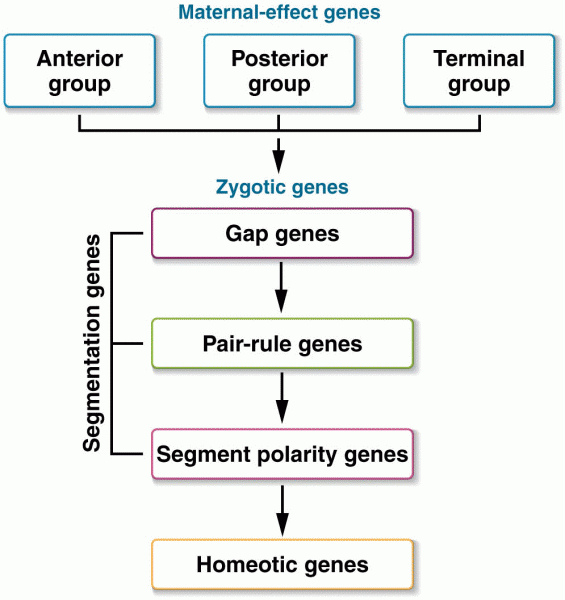
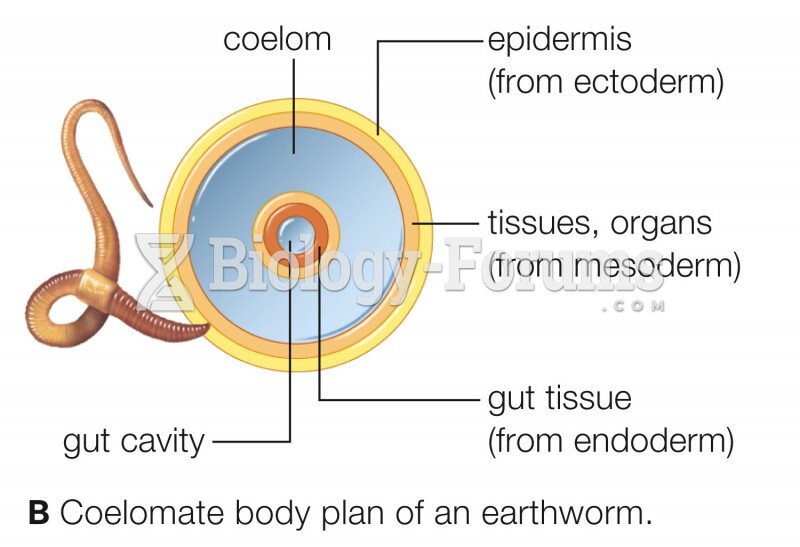
|
|
|
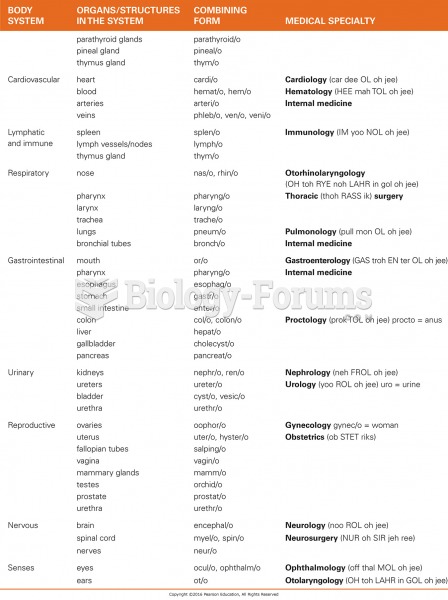
Children with strabismus (crossed eyes) can be treated. They are not able to outgrow this condition on their own, but with help, it can be more easily corrected at a younger age. It is important for infants to have eye examinations as early as possible in their development and then another at age 2 years.
The toxic levels for lithium carbonate are close to the therapeutic levels. Signs of toxicity include fine hand tremor, polyuria, mild thirst, nausea, general discomfort, diarrhea, vomiting, drowsiness, muscular weakness, lack of coordination, ataxia, giddiness, tinnitus, and blurred vision.
In 2010, opiate painkllers, such as morphine, OxyContin®, and Vicodin®, were tied to almost 60% of drug overdose deaths.
Ether was used widely for surgeries but became less popular because of its flammability and its tendency to cause vomiting. In England, it was quickly replaced by chloroform, but this agent caused many deaths and lost popularity.
Throughout history, plants containing cardiac steroids have been used as heart drugs and as poisons (e.g., in arrows used in combat), emetics, and diuretics.