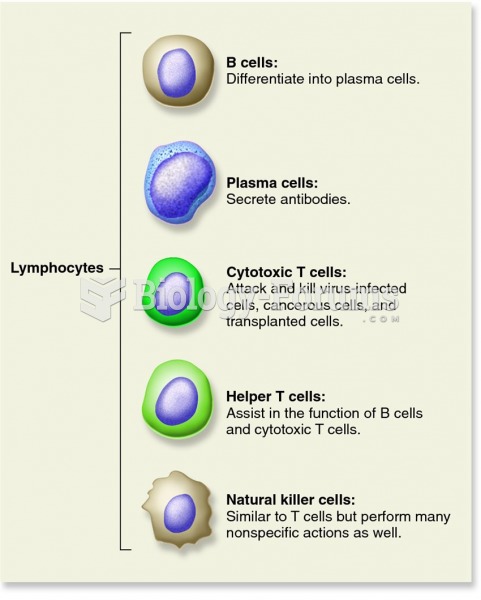
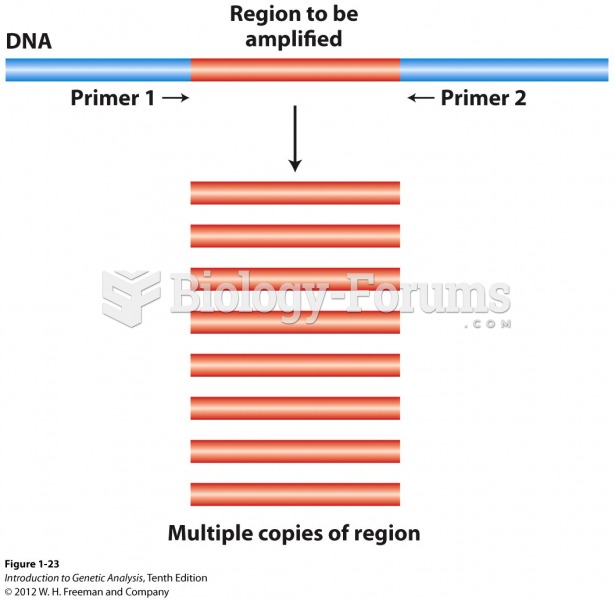
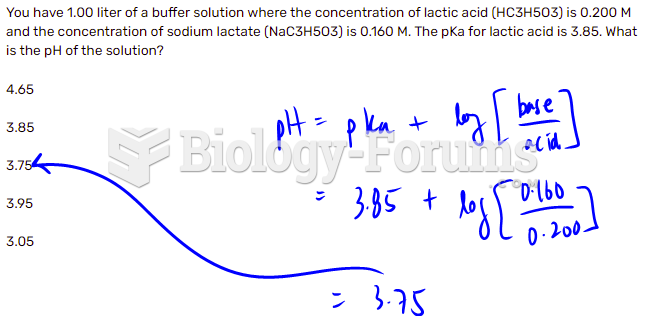
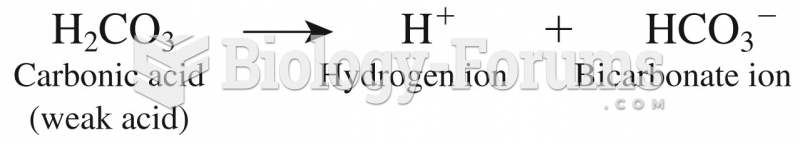|
|
|
The National Institutes of Health have supported research into acupuncture. This has shown that acupuncture significantly reduced pain associated with osteoarthritis of the knee, when used as a complement to conventional therapies.
More than nineteen million Americans carry the factor V gene that causes blood clots, pulmonary embolism, and heart disease.
Stroke kills people from all ethnic backgrounds, but the people at highest risk for fatal strokes are: black men, black women, Asian men, white men, and white women.
Medication errors are three times higher among children and infants than with adults.
Acetaminophen (Tylenol) in overdose can seriously damage the liver. It should never be taken by people who use alcohol heavily; it can result in severe liver damage and even a condition requiring a liver transplant.