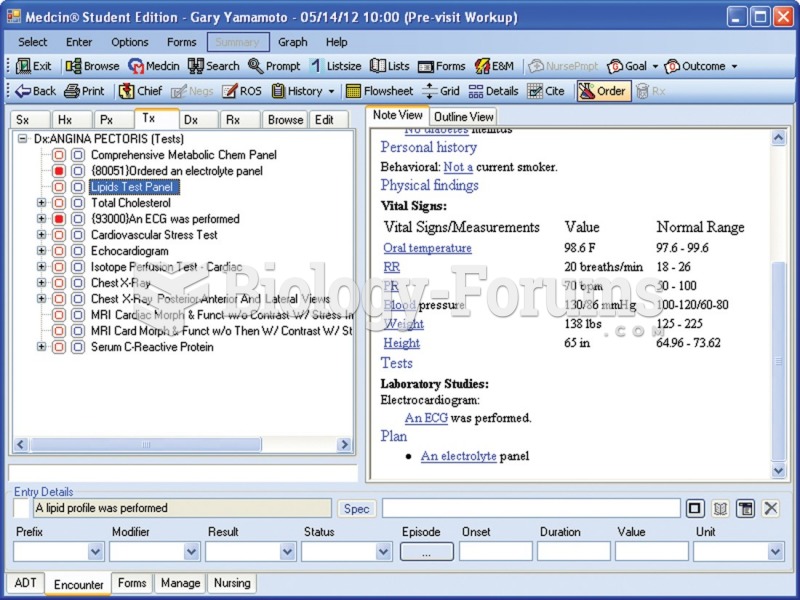
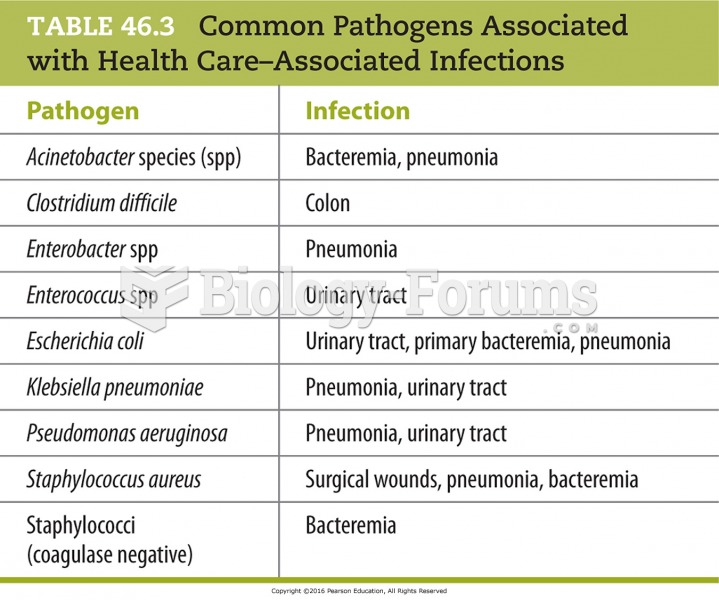
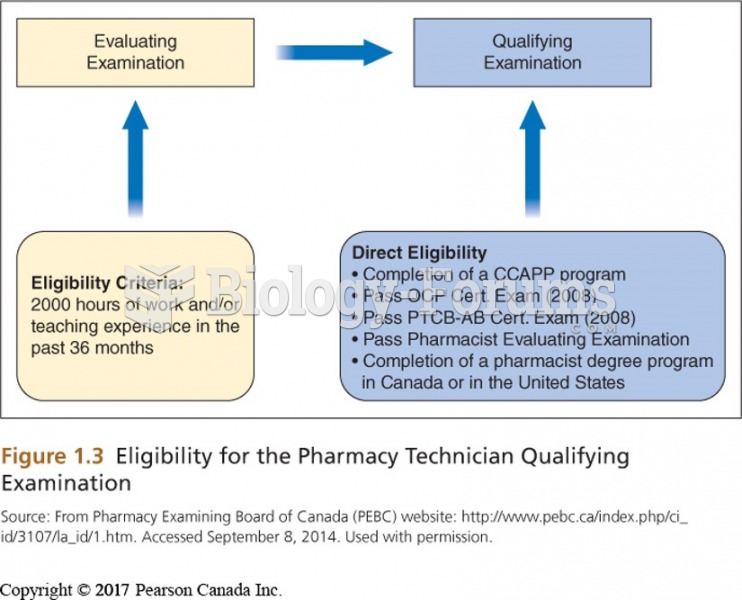
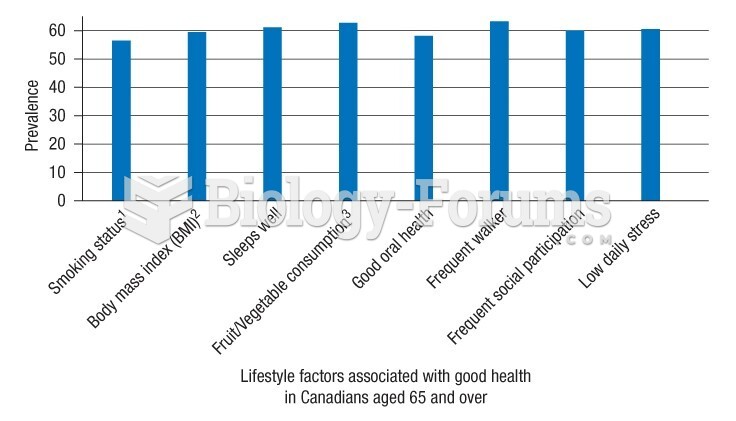
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
During the twentieth century, a variant of the metric system was used in Russia and France in which the base unit of mass was the tonne. Instead of kilograms, this system used millitonnes (mt).
Did you know?
If you could remove all of your skin, it would weigh up to 5 pounds.
Did you know?
The Romans did not use numerals to indicate fractions but instead used words to indicate parts of a whole.
Did you know?
There are more sensory neurons in the tongue than in any other part of the body.
Did you know?
Approximately one in three babies in the United States is now delivered by cesarean section. The number of cesarean sections in the United States has risen 46% since 1996.