|
|
|
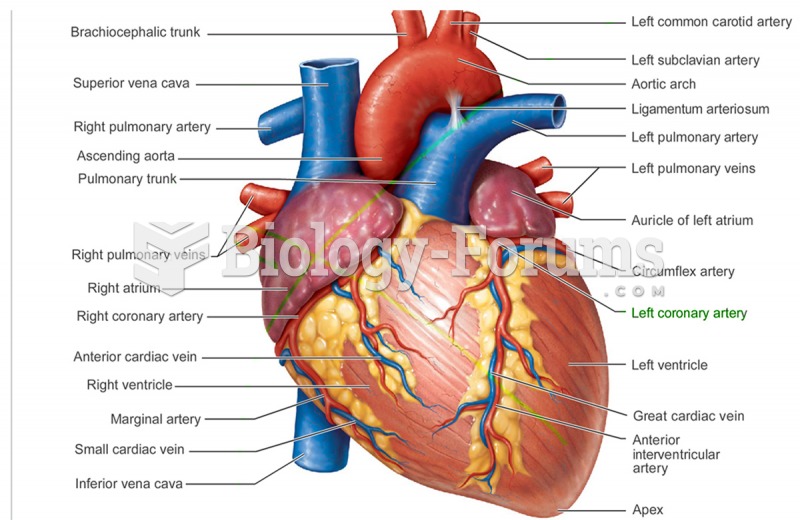
The heart is located in the center of the chest, with part of it tipped slightly so that it taps against the left side of the chest.
Inotropic therapy does not have a role in the treatment of most heart failure patients. These drugs can make patients feel and function better but usually do not lengthen the predicted length of their lives.
No drugs are available to relieve parathyroid disease. Parathyroid disease is caused by a parathyroid tumor, and it needs to be removed by surgery.
Throughout history, plants containing cardiac steroids have been used as heart drugs and as poisons (e.g., in arrows used in combat), emetics, and diuretics.
In most climates, 8 to 10 glasses of water per day is recommended for adults. The best indicator for adequate fluid intake is frequent, clear urination.