|
|
|
Only one in 10 cancer deaths is caused by the primary tumor. The vast majority of cancer mortality is caused by cells breaking away from the main tumor and metastasizing to other parts of the body, such as the brain, bones, or liver.
Amoebae are the simplest type of protozoans, and are characterized by a feeding and dividing trophozoite stage that moves by temporary extensions called pseudopodia or false feet.
The most destructive flu epidemic of all times in recorded history occurred in 1918, with approximately 20 million deaths worldwide.
ACTH levels are normally highest in the early morning (between 6 and 8 A.M.) and lowest in the evening (between 6 and 11 P.M.). Therefore, a doctor who suspects abnormal levels looks for low ACTH in the morning and high ACTH in the evening.
In the United States, congenital cytomegalovirus causes one child to become disabled almost every hour. CMV is the leading preventable viral cause of development disability in newborns. These disabilities include hearing or vision loss, and cerebral palsy.
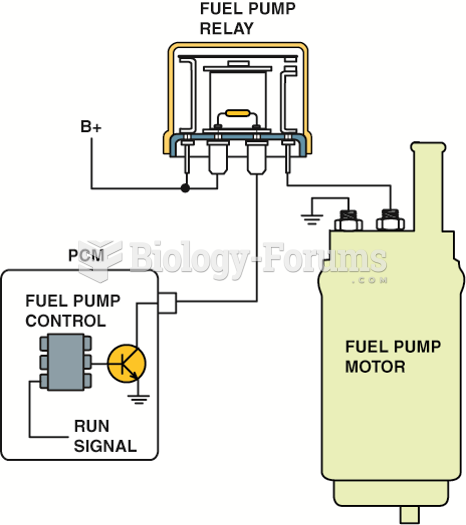 A typical low-side driver (LSD) which uses a control module to control the ground side of the relay ...
A typical low-side driver (LSD) which uses a control module to control the ground side of the relay ...
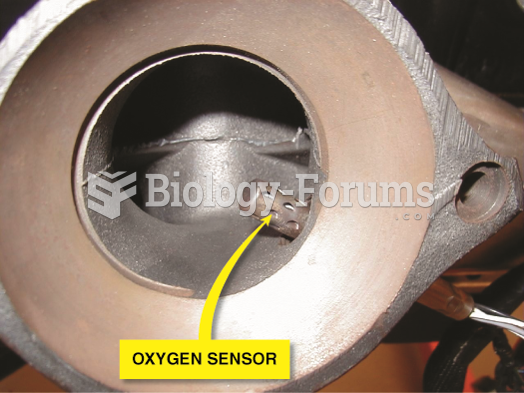 Many fuel-control oxygen sensors are located in the exhaust manifold near its outlet so that the ...
Many fuel-control oxygen sensors are located in the exhaust manifold near its outlet so that the ...