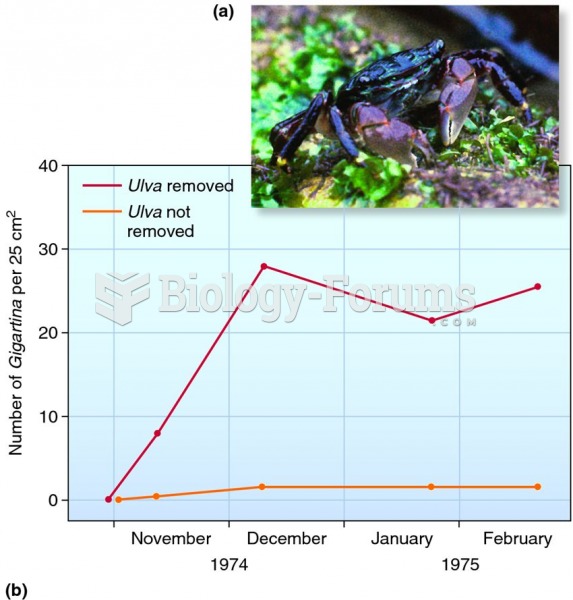
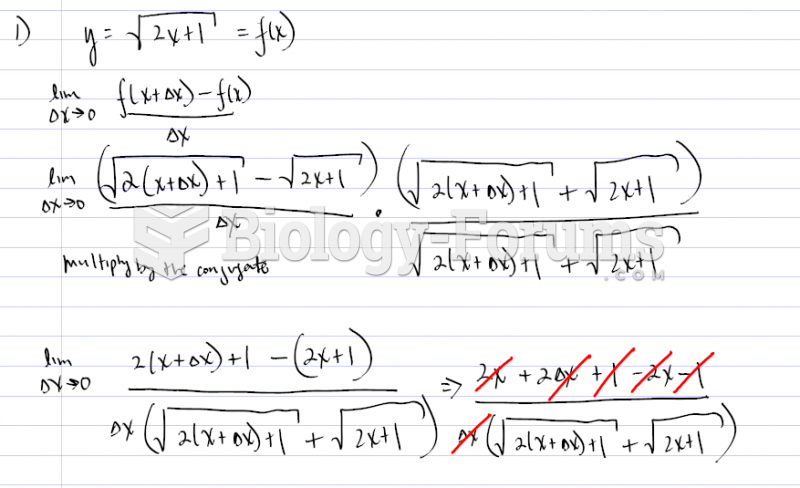
|
|
|
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus or MRSA was discovered in 1961 in the United Kingdom. It if often referred to as a superbug. MRSA infections cause more deaths in the United States every year than AIDS.
Signs of depression include feeling sad most of the time for 2 weeks or longer; loss of interest in things normally enjoyed; lack of energy; sleep and appetite disturbances; weight changes; feelings of hopelessness, helplessness, or worthlessness; an inability to make decisions; and thoughts of death and suicide.
Though newer “smart” infusion pumps are increasingly becoming more sophisticated, they cannot prevent all programming and administration errors. Health care professionals that use smart infusion pumps must still practice the rights of medication administration and have other professionals double-check all high-risk infusions.
The average adult has about 21 square feet of skin.
Today, nearly 8 out of 10 pregnant women living with HIV (about 1.1 million), receive antiretrovirals.