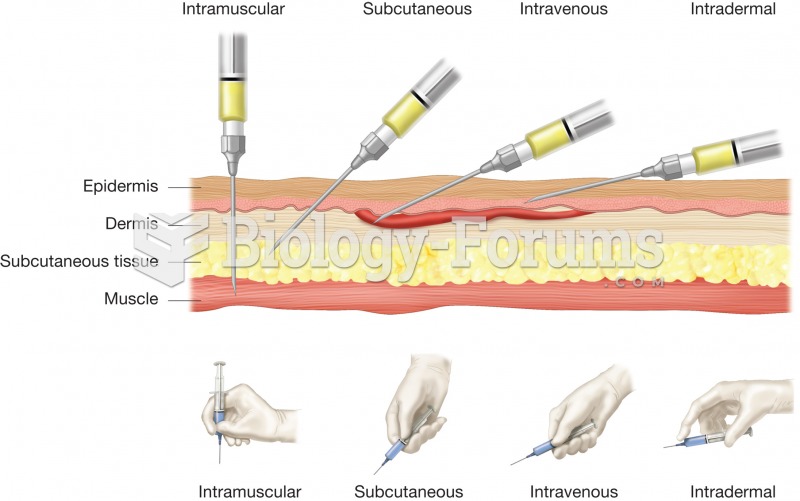
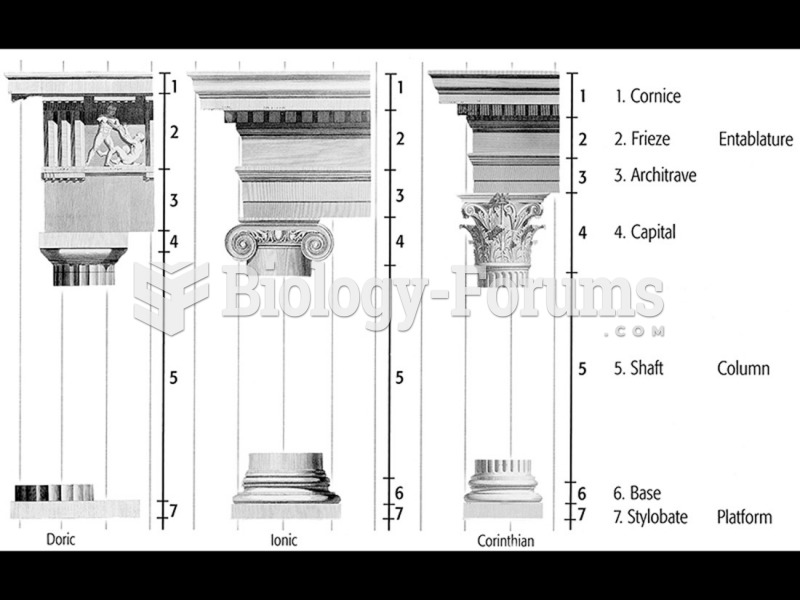
|
|
|
After a vasectomy, it takes about 12 ejaculations to clear out sperm that were already beyond the blocked area.
The senior population grows every year. Seniors older than 65 years of age now comprise more than 13% of the total population. However, women outlive men. In the 85-and-over age group, there are only 45 men to every 100 women.
The heart is located in the center of the chest, with part of it tipped slightly so that it taps against the left side of the chest.
In 2006, a generic antinausea drug named ondansetron was approved. It is used to stop nausea and vomiting associated with surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.
Street names for barbiturates include reds, red devils, yellow jackets, blue heavens, Christmas trees, and rainbows. They are commonly referred to as downers.