|
|
|
Malaria mortality rates are falling. Increased malaria prevention and control measures have greatly improved these rates. Since 2000, malaria mortality rates have fallen globally by 60% among all age groups, and by 65% among children under age 5.
Asthma-like symptoms were first recorded about 3,500 years ago in Egypt. The first manuscript specifically written about asthma was in the year 1190, describing a condition characterized by sudden breathlessness. The treatments listed in this manuscript include chicken soup, herbs, and sexual abstinence.
Every 10 seconds, a person in the United States goes to the emergency room complaining of head pain. About 1.2 million visits are for acute migraine attacks.
Cancer has been around as long as humankind, but only in the second half of the twentieth century did the number of cancer cases explode.
People about to have surgery must tell their health care providers about all supplements they take.
 As a result of sharing its environment with humans, this macaque had the opportunity to steal an ast
As a result of sharing its environment with humans, this macaque had the opportunity to steal an ast
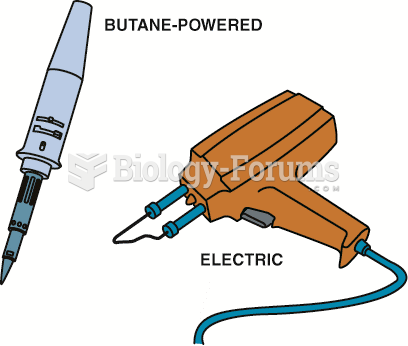 Electric and butane-powered soldering guns used to make electrical repairs. Soldering guns are sold ...
Electric and butane-powered soldering guns used to make electrical repairs. Soldering guns are sold ...