|
|
|
About one in five American adults and teenagers have had a genital herpes infection—and most of them don't know it. People with genital herpes have at least twice the risk of becoming infected with HIV if exposed to it than those people who do not have genital herpes.
Cyanide works by making the human body unable to use oxygen.
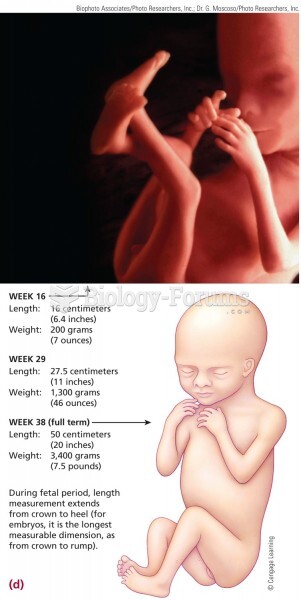
The largest baby ever born weighed more than 23 pounds but died just 11 hours after his birth in 1879. The largest surviving baby was born in October 2009 in Sumatra, Indonesia, and weighed an astounding 19.2 pounds at birth.
About 80% of major fungal systemic infections are due to Candida albicans. Another form, Candida peritonitis, occurs most often in postoperative patients. A rare disease, Candida meningitis, may follow leukemia, kidney transplant, other immunosuppressed factors, or when suffering from Candida septicemia.
GI conditions that will keep you out of the U.S. armed services include ulcers, varices, fistulas, esophagitis, gastritis, congenital abnormalities, inflammatory bowel disease, enteritis, colitis, proctitis, duodenal diverticula, malabsorption syndromes, hepatitis, cirrhosis, cysts, abscesses, pancreatitis, polyps, certain hemorrhoids, splenomegaly, hernias, recent abdominal surgery, GI bypass or stomach stapling, and artificial GI openings.