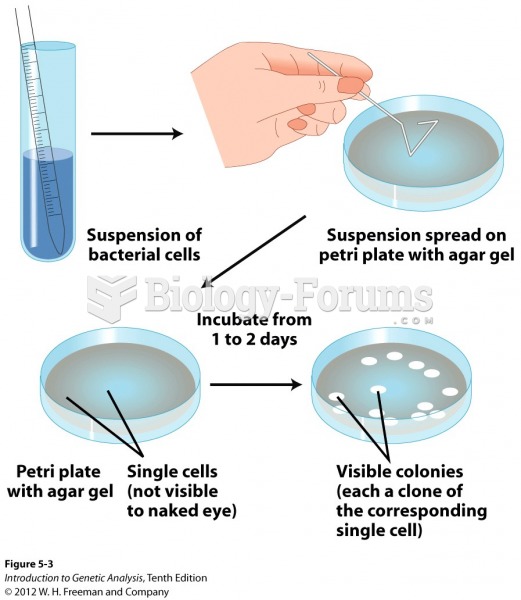
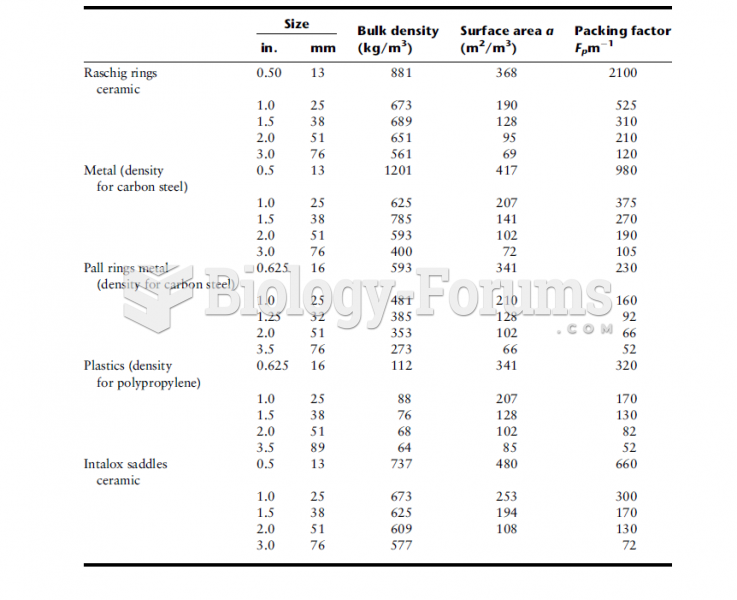
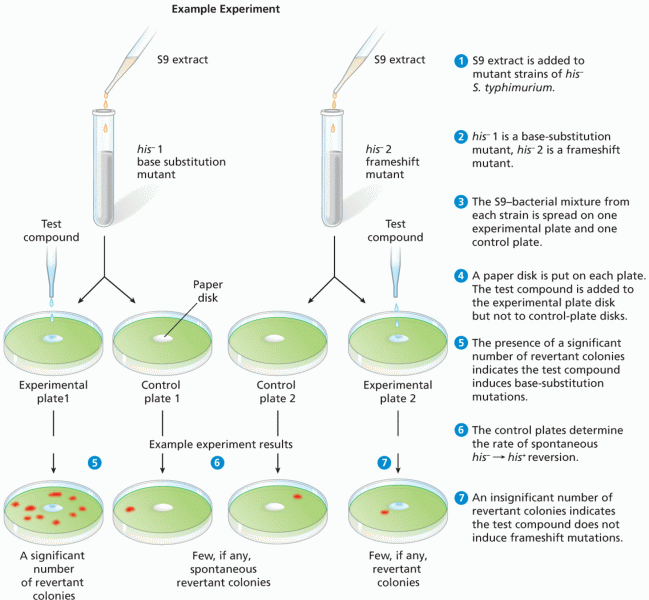
|
|
|
When intravenous medications are involved in adverse drug events, their harmful effects may occur more rapidly, and be more severe than errors with oral medications. This is due to the direct administration into the bloodstream.
The Babylonians wrote numbers in a system that used 60 as the base value rather than the number 10. They did not have a symbol for "zero."
People with alcoholism are at a much greater risk of malnutrition than are other people and usually exhibit low levels of most vitamins (especially folic acid). This is because alcohol often takes the place of 50% of their daily intake of calories, with little nutritional value contained in it.
People with high total cholesterol have about two times the risk for heart disease as people with ideal levels.
Side effects from substance abuse include nausea, dehydration, reduced productivitiy, and dependence. Though these effects usually worsen over time, the constant need for the substance often overcomes rational thinking.